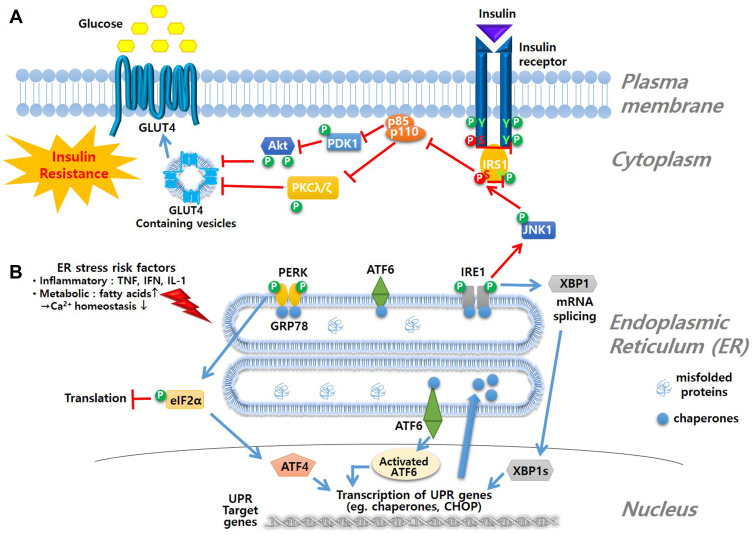
Figure 3.
Mechanism of ER stress and insulin resistance. (A) insulin signal pathway is blocked due to ER stress-induced phosphorylation of JNK1 followed by phosphorylation of serine moiety of IRS1 to inhibit glucose influx as a result (B) ER stress is triggered by various risk factors that interrupt Ca2+ homeostasis. Accumulation of misfolded proteins in lumen of ER induces ER-resident membrane sensor molecules, such as PERK, ATF6 and IRE1, to initiate the UPR signal starting with dimerization and autophosphorylation of the sensing molecules. UPR signals lead to inhibition of translation, activation of UPR genes such as chaperones and CHOP, or degradation of misfolded protein by ER-associated protein degradation (ERAD) process.