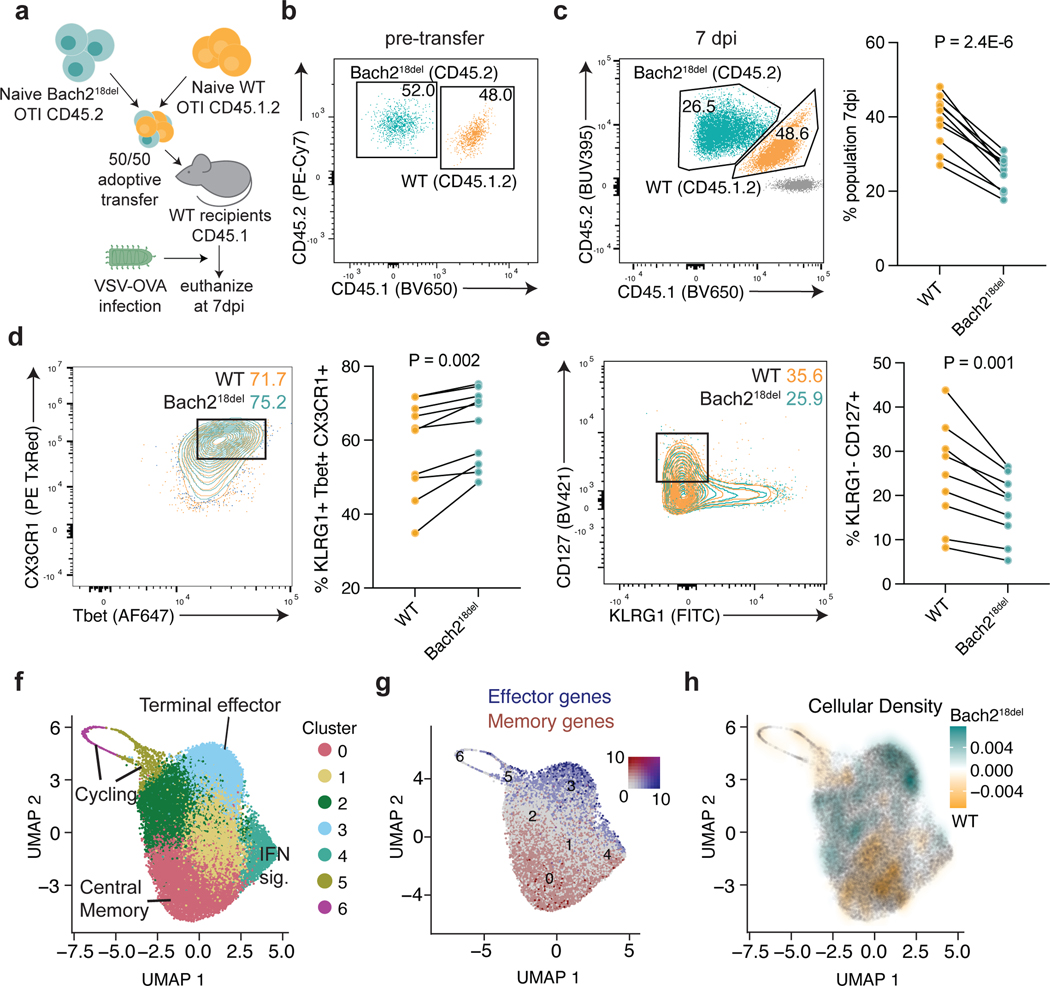
Fig. 6. Bach218del CD8 T cells are more prone to effector T cell differentiation post-acute viral infection.
a) Experimental setup for OTI T cell co-transfer system. 5,000 congenically-marked naïve CD8 OTI T cells from WT and Bach218del were co-transferred into congenically-marked recipient mice, which were subsequently infected with VSV-OVA. Mice were euthanized 7 days post-infection (7 dpi) for flow cytometry analysis. b) Analysis of WT and Bach218del cell frequencies pre-transfer. c) Relative frequency of WT and Bach218del cell percentages post-transfer and 7 dpi. d) Frequency of CD8+CD44+KLRG1+CD127-Tbet+CX3CR1+ effector T cells at 7 dpi. e) Frequency of CD8+ CD44+CD127+KLRG1- memory precursors at 7 dpi. f) UMAP and cluster analysis of OTI WT and Bach218del single cell RNA-seq at 8 dpi. g) UMAP plot showing expression of effector (Klrg1, Gzmb, Zeb2) and memory (Il7r, Ccr7, Tcf7, Sell) genes in blue and red, respectively. h) UMAP plot showing relative cellular density enrichment of Bach218del vs. WT cells. For (c-e), n = 10 biologically independent animals per experiment examined over 2 experiments and P values were determined by Student’s two-sided paired t-test.