Figure 2. Identification of anti-biofouling acrylamide-based copolymer combinations.
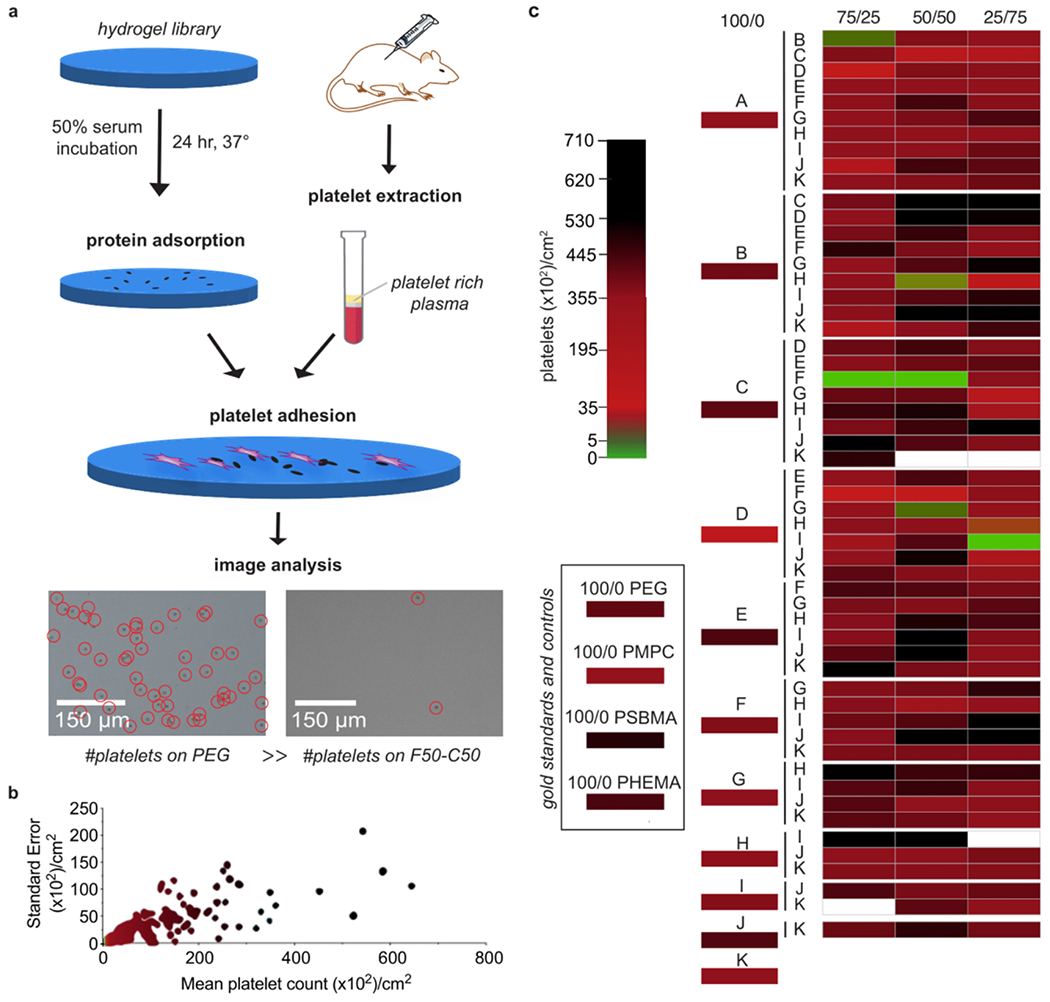
a. Hydrogel samples were first incubated in 50% fetal bovine serum for 24 hr at 37 °C to ensure extensive protein adsorption to the samples. Platelet rich plasma (PRP) obtained from centrifugation of rat blood was then incubated on the surface of the hydrogels for 1 hr at 37 °C. Several polyacrylamide copolymer hydrogels presented significantly less platelet adhesion than PEG, PHEMA, and polyzwitterionic hydrogel controls. b. Standard error versus mean of the platelet count distribution obtained for each copolymer hydrogel. c. Heat map of median platelet adhesion counts on copolymer hydrogel samples, ordered by the weight ratio of each monomer in the hydrogel formulation (100/0, 25/75, 50/50, 75/25). Colors were assigned to the medians obtained in n ≥ 3 tests.
