Extended Data Fig. 6. Chromatin accessibility profiling of LCMV-specific CD8+ T cells in acute and chronic infection and after PD-1 treatment, IL-2 or PD-1 + IL-2 combination therapy.
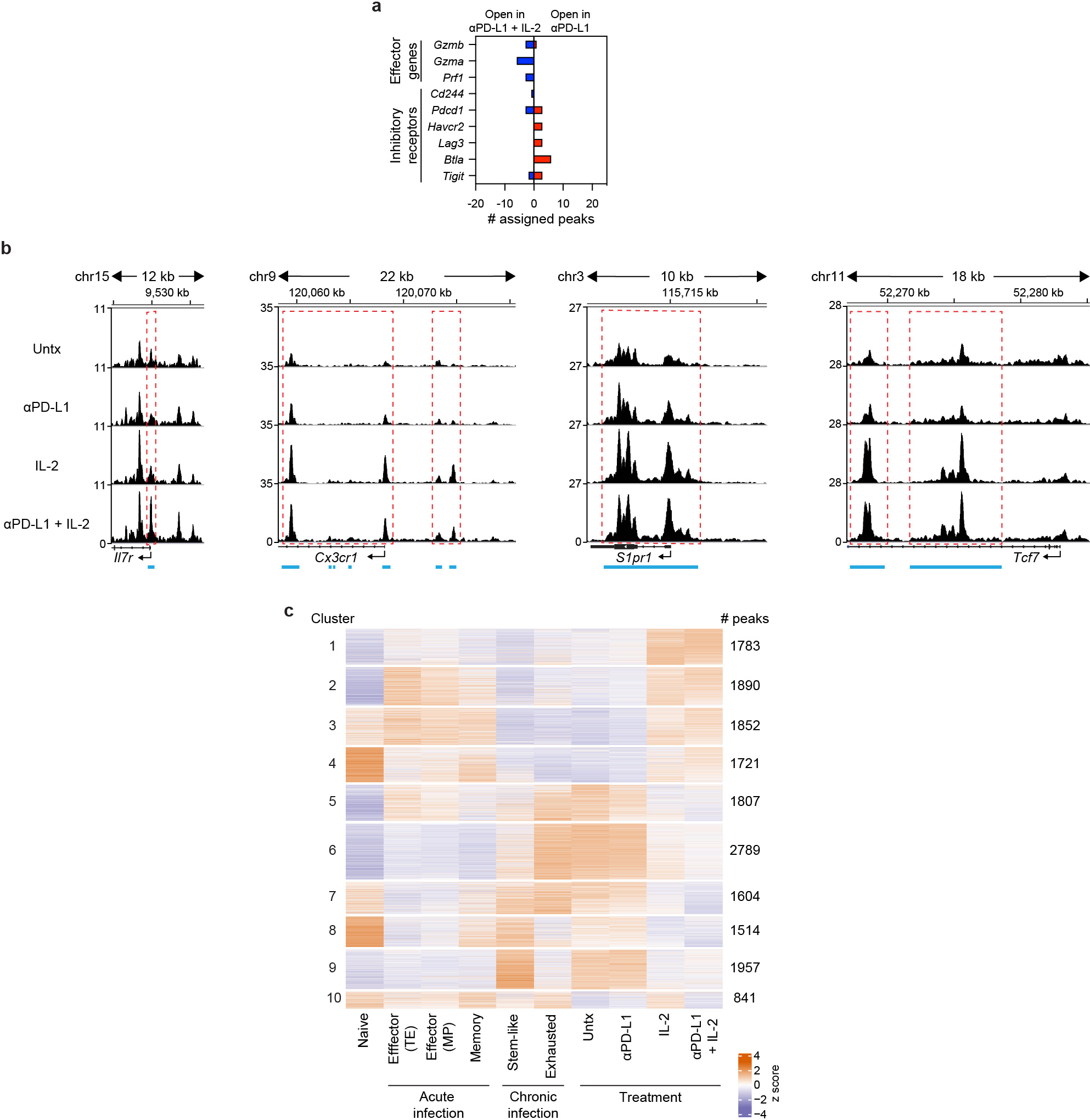
a, Gene annotations of differentially accessible distal regulatory regions in DbGP33+ CD8+ T cells of mice treated with anti-PD-L1 and PD-1 + IL-2 combination therapy. The number of differentially open gene regulatory regions for genes of functional importance in DbGP33+ CD8+ T cells after PD-1 monotherapy vs. PD-1 + IL-2 combination therapy is shown. b, Accessibility tracks for representative genes in LCMV-specific DbGP33+ CD8+ T cells generated by various treatments during chronic infection. Light blue lines beneath each panel indicate differentially accessible regions in DbGP33+ CD8+ T cells generated by PD-1 therapy versus PD-1 + IL-2 combination therapy. Red dotted lines highlight the regions indicated by the light blue lines. c, Heat map with 10 clusters generated by using k-means clustering of 16,758 DARs among DbGP33+ CD8+ T cells generated by the combination therapy. Then, naive CD8+ T cells and various LCMV-specific CD8+ T-cell subsets during acute and chronic infections were incorporated into the heat map. Results were pooled from 3 experiments of ATAC-seq with n = 12–18 for untreated mice or n = 1–3 for treatment samples per group in each experiment. ATAC-seq data for naive, acute (memory precursor (MP), terminal effector (TE), and memory), and chronic (stem-like and exhausted) was from our previous study30. Untx, untreated.
