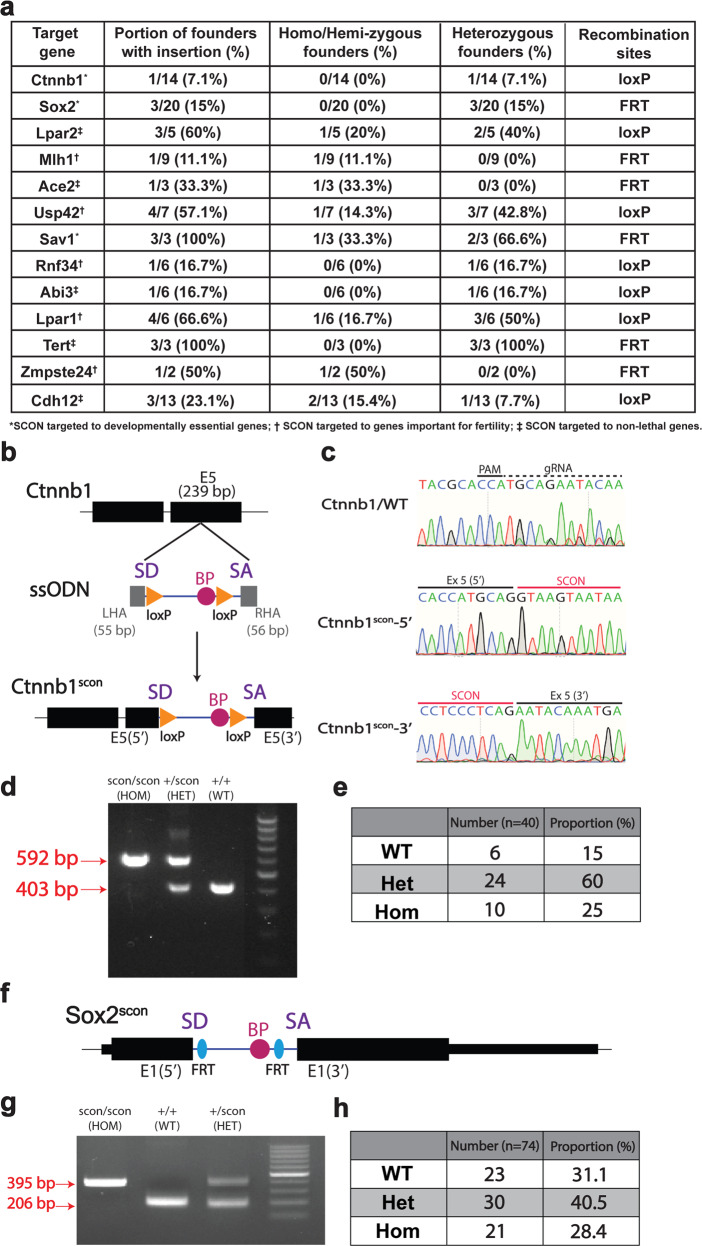
Fig. 4. SCON mice can be generated via one-step embryo injection, and SCON is tolerated in homozygosity.
a List of alleles successfully targeted with SCON and the corresponding efficiencies, genotypes, and recombination sites used. b Schematic illustration of SCON targeting ssODN, with 55 and 56 bp left and right homology arms, respectively, in exon 5 of the Ctnnb1 gene. c Sanger sequencing track of the WT, 5′ and 3′ alleles of Ctnnb1 and Ctnnb1scon, respectively. d Genotyping PCR of Ctnnb1scon/scon (HOM), Ctnnb1+/scon (HET), and Ctnnb1+/+ (WT), in which the lower (403 bp) and upper (592 bp) bands correspond to the WT and knock-in alleles, respectively. e Genotype quantification from crosses of double heterozygotes (Ctnnb1+/scon). Total number of offspring, n = 40. f Schematic illustration of the Sox2scon allele. g Genotyping PCR of Sox2scon/scon (HOM), Sox2+/+ (WT), and Sox2+/scon (HET), in which the lower (206 bp) and upper (395 bp) bands correspond to the WT and knock-in alleles, respectively. h Genotyping quantification from crosses of heterozygotes (Sox2+/scon). Total number of offspring, n = 74.