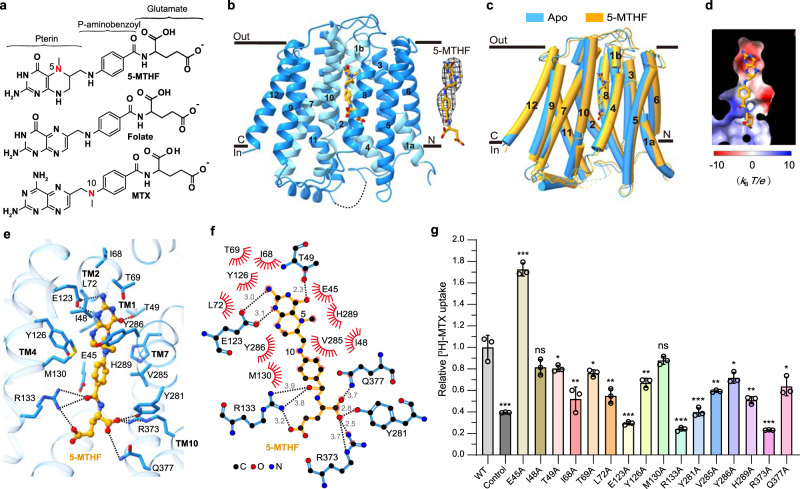
Fig. 2. Cryo-EM structure of the SLC19A1/5-MTHF complex.
a Chemical structures of several folate analogs: 5-MTHF, folate, and MTX. The constituent moieties of 5-MTHF are indicated. b Ribbon diagram of SLC19A1 in complex with 5-MTHF. The four TMs (TM1, 4, 7, and 10) interacting with 5-MTHF are colored in cyan and the other ones are colored in blue. 5-MTHF is shown in sticks and its cryo-EM densities are shown in black meshes. c Superposition of the apo and 5-MTHF-bound SLC19A1 structures. d The electrostatic potential (in units of kBT/e, where kB is the Boltzmann constant, T is the absolute temperature and e is the elementary charge) of the substrate-binding pocket in SLC19A1, as calculated at pH 7.0 and 0.15 M concentrations of monovalent cations and anions. 5-MTHF is shown in sticks. e Ribbon presentation of the substrate-binding site in SLC19A1. The residues participating in 5-MTHF binding are indicated with side chains (< 4.0 Å). Hydrogen bonds and salt bridges are depicted as dashed lines. f A schematic summary of the interactions between SLC19A1 and 5-MTHF. The distances of the hydrogen bonds are indicated in angstroms. g The [3H]-MTX uptake activities of SLC19A1 mutants. The results are normalized to the activity of wild-type SLC19A1. All experiments were done in triplicates (n = 3, mean ± SD). ns, non-significant; * P < 0.01; ** P < 0.005; *** P < 0.001 (Student’s t-test).