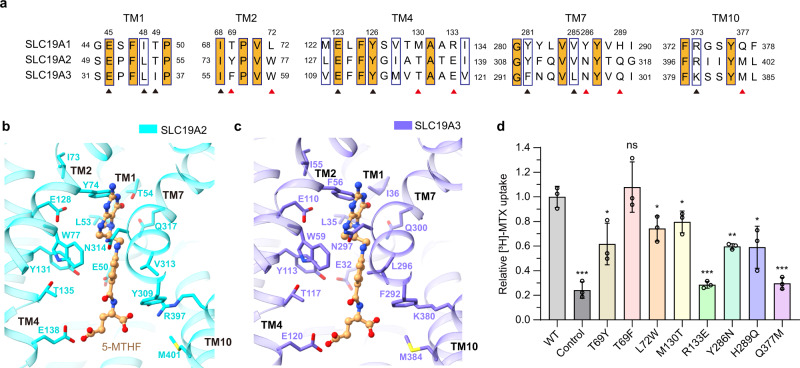
Fig. 3. Analyses of the substrate discrimination mechanism of SLC19 subfamily members.
a Sequence alignment of the three SLC19 family members. The partially conserved residues are indicated with blue boxes and the strictly conserved ones are further filled with orange color. The residues of SLC19A1 that are involved in 5-MTHF binding are indicated. The conserved and non-conserved ones are denoted by black and red arrowheads, respectively. b, c Ribbon presentation of the 5-MTHF binding site in SLC19A2 and SLC19A3. The structures of SLC19A2 and SLC19A3 are predicted by AlphaFold. 5-MTHF is modeled into these structures based on the superposition with our SLC19A1/5-MTHF structure. The cognates of SLC19A2 and SLC19A3 corresponding to the 5-MTHF interaction residues of SLC19A1 are indicated. d Functional verification of the non-conserved residues for SLC19A1 using the [3H]-MTX uptake assay. The results are normalized to the activity of wild-type SLC19A1. All experiments were done in triplicates (n = 3, mean ± SD). ns, non-significant; * P < 0.01; ** P < 0.005; *** P < 0.001 (Student’s t-test).