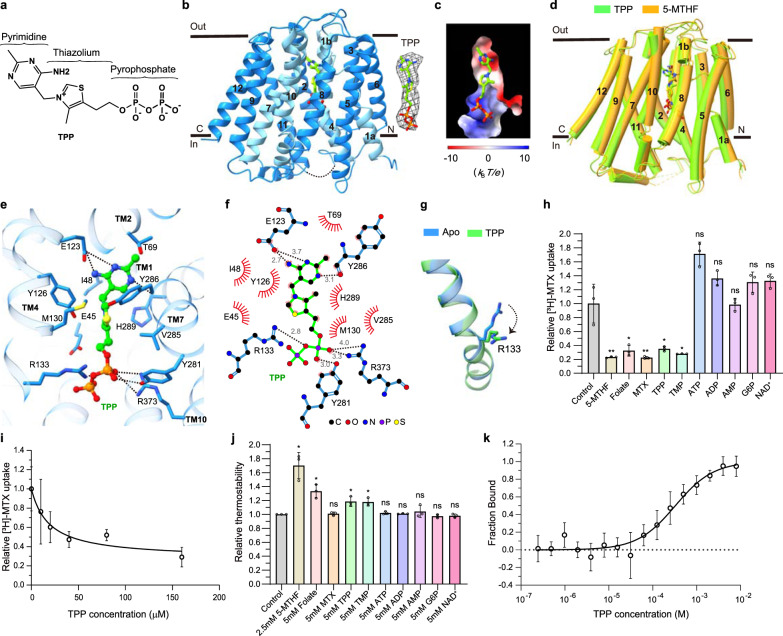
Fig. 4. Verification of TPP as the favorite coupled substrate of SLC19A1.
a The chemical structure of TPP. The constituent moieties are indicated. b Ribbon diagram of SLC19A1 in complex with TPP. TPP is shown in sticks and its cryo-EM densities are shown in black meshes. c The electrostatic potential of the TPP binding site. d Structural comparison of the TPP- and 5-MTHF-bound SLC19A1. e Ribbon presentation of the TPP-binding site in SLC19A1. The residues involved in the interaction with TPP are shown with side chains. f A schematic summary of the interactions between SLC19A1 and TPP. The distances of the hydrogen bonds are indicated in angstroms. g Conformational change of the side chain of Arg133 between apo and TPP-bound SLC19A1 structures. h Inhibitory effect of different compounds on the [3H]-MTX uptake activity of SLC19A1. All the molecules were tested at a concentration of 200 μM. The results are normalized to the activity of the control experiment in which no inhibitors are added. All experiments were done in triplicates (n = 3, mean ± SD). ns, non-significant; * P < 0.01; ** P < 0.005 (Student’s t-test). i Quantitative measurement of the potency of TPP in inhibiting the [3H]-MTX delivery by SLC19A1. The results are normalized to the MTX transport activity of SLC19A1 in the absence of TPP. All experiments were done in triplicates (n = 3, mean ± SD). IC50 was calculated by fitting to a nonlinear regression model. j Quantification of the fluorescence-detection size-exclusion chromatography (FSEC)-based thermostability assay. The concentrations of molecules are indicated. The thermostability is calculated relative to the control experiment in which SLC19A1 was not incubated with any compounds. All experiments were done in triplicates (n = 3, mean ± SD). ns, non-significant; * P < 0.01 (Student’s t-test). k MST analysis to examine the affinity of SLC19A1 for TPP. All experiments were done in multiple replicates (n = 6–10, mean ± SD).