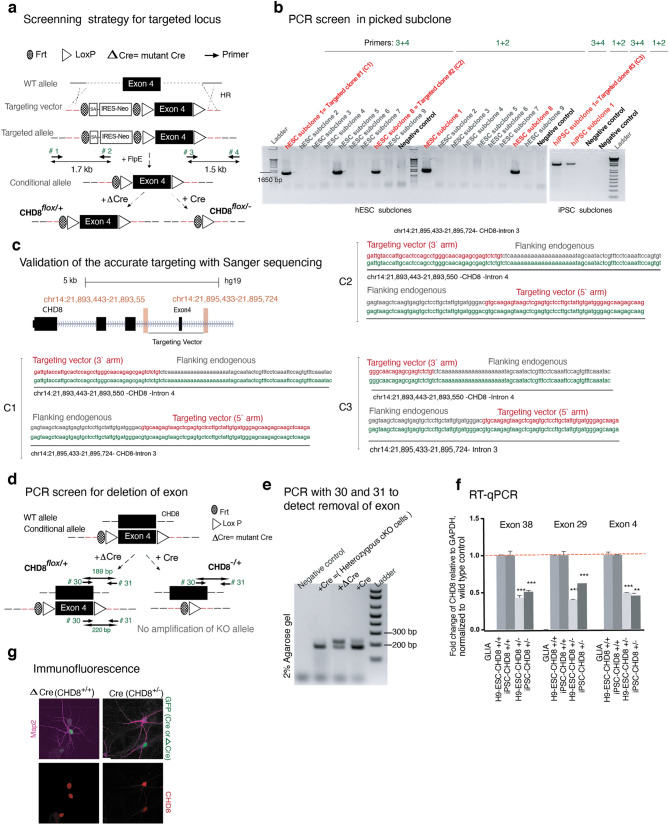
Figure 2.
Targeting and characterizing conditional heterozygous CHD8 knockout stem cell lines. (a) Schematics of Targeting strategy for generating a conditional KO allele of the CHD8 gene by flanking exon 4 with LoxP sites (similar to Fig. 1a with the inclusion of the ‘screening’ primers). Deletion of exon four is predicted to create a frameshift mutation with early truncation. (b) Screening PCR using external primers designed for outside the homology arm towards inside the targeting vector identified two subclones from the hESC line (C1 & C2) and one subclone from the iPSC line (C3) that were positive for the insertion of the targeting vector. (c) Sanger sequencing is spanning the targeting arms' transition into endogenous sequences, demonstrating correct targeting of the construct into the CHD8 locus (clones C1, C2, and C3). (d, e) Excision of exon four after infection with LV-Cre and screening with the primers around the loxP sites (primer 30 and primer 31) resulted in a single band from heterozygous KO compared to two bands in WT cells as expected. (f) Quantitative reverse transcription PCR (RT-qPCR) using the probes for three exons of CHD8 gene shows the levels of mRNA decreases in heterozygous KO neurons. (g) Immunofluorescence analysis of heterozygous KO and WT neurons for Map2 and CHD8. The nuclear staining signal intensity significantly decreases in heterozygous mutant neurons.