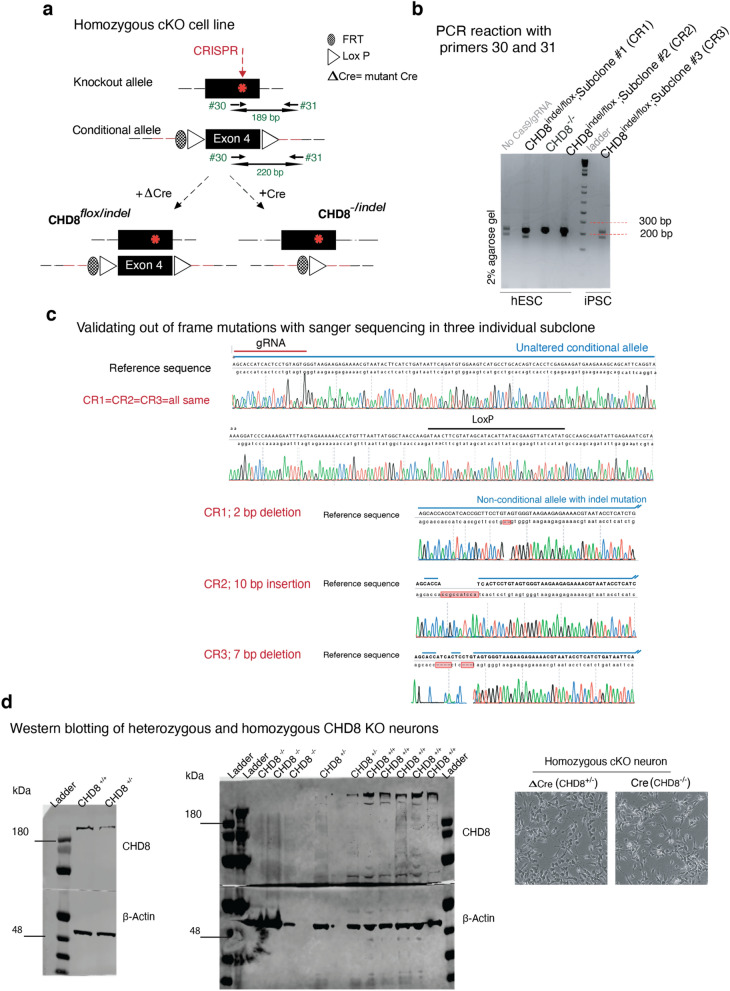
Figure 3.
Targeting conditional homozygous CHD8 knockout stem cell lines. (a) Introduction of an indel mutation by CRISPR-CAS9 to non-conditional exon 4 of CHD8 gene, to generate a conditional homozygous knock out cells. (b) Validation of the genotype by PCR around the loxP sequence (spanning the gRNA targeting region) and amplification of two bands; one allele is 32 bp smaller than the other allele. Therefore, the top band corresponds to the floxed allele, and the bottom band is the non-conditional allele, a candidate for carrying an indel mutation. Each band is cut and gel-purified, TOPO cloned, and sequenced using M13 forward and M13 reverse primers (CR1, CR2; both hESC and CR3, is an iPSC subclone, confirmed to carry an indel mutation in non-floxed allele). (c) Sanger sequencing of floxed and non-floxed alleles identified three subclones that carry frameshift indel mutations in the non-conditional allele with an un-altered floxed allele. Note that the conditional exon is shown only once as the representative sequence for all three subclones. (d) Western blotting of heterozygous and homozygous CHD8 knockout neurons reveals a decrease in total protein compared to the control condition (shows two independent replicates). The Right is the phase-contrast images of day 5 neurons and shows cultures of KO and control cells are indistinguishable.