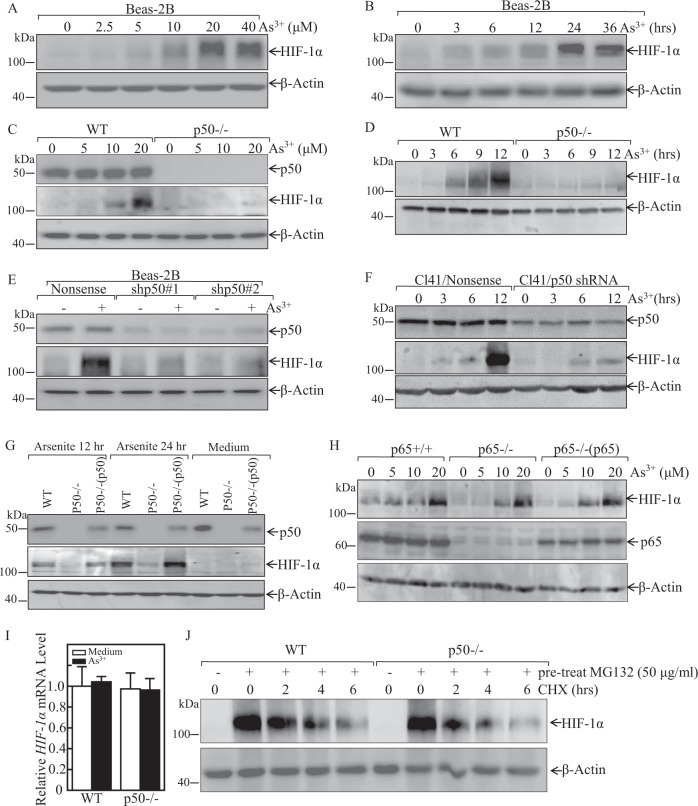
Fig. 1. p50, but not p65, was required for arsenite-induced HIF-1α protein expression following arsenite treatment.
A, B Beas-2B cells were treated with various doses of arsenite for 24 h or 20 μM arsenite for the indicated time periods. The cells were then extracted and subjected to western blot assay. C, D WT and p50−/− cells were exposed to indicated concentration arsenite for 24 h (C), or were treated with 20 μM arsenite for the indicated times (D). The cells were then extracted and subjected to western blot assay. E, F Beas-2B cells and mouse epidermal Cl41 cells were stably transfected with shRNA p50, these transfectants were then treated with 20 μM arsenite for 24 h (E) or for different time points (F) as indicated; The cell extracts were subjected to western blot by using indicated antibodies. G WT, p50−/−, and p50−/−(p50) cells were exposed to 20 μM arsenite for 12 h or 24 h; H p65+/+, p65−/−, and p65−/−(p65) cells were treated with arsenite at indicated doses for 24 h. Whole-cell extracts from each of above experiments were subjected to western blot for the determination of protein expression of p50, p65, and HIF-1α. β-Actin was used as protein loading control. I WT and p50−/− cells were exposed to 20 μM arsenite and the HIF-1α mRNA expression was determined by Real-Time PCR; J WT and p50−/− cells were pretreated with 50 μM of MG132 for 10 h, then these cells were exposed to 50 μg/ml CHX for the times indicated after removal of MG132, and the cell extracts were subjected to western blot for the determination of protein expression of HIF-1α. β-Actin was used as protein loading control.