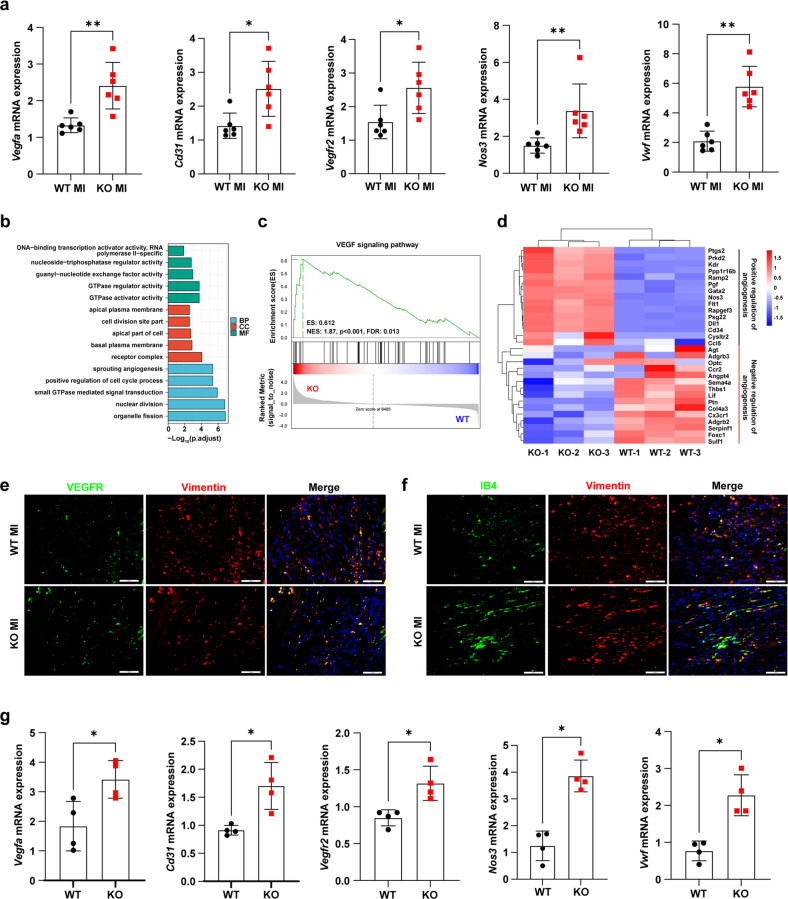
Fig. 6. KDM5B deficiency facilitates angiogenesis via the transition of fibroblasts to endothelial-like cells.
a Q-PCR analysis of Vegfa, Cd31, Vegfr2, Nos3 and Vwf mRNA levels in myocardial tissues from KDM5B-KO or WT mice on Day 7 after MI surgery (n = 6 mice per group). b Gene Ontology enrichment analysis showing the top 15 differentially expressed genes in primary cardiac fibroblasts isolated from the heart tissues of KDM5B-KO and littermate control WT mice on Day 7 after MI surgery (BP biological process, CC cellular component, MF molecular function). c GSEA enrichment plot showing gene sets associated with the VEGF signaling pathway in primary cardiac fibroblasts as in b. d Heatmap showing differentially expressed genes relative to the positive and negative regulation of angiogenesis in primary cardiac fibroblasts as in b. e, f Representative immunofluorescence staining of VEGFR (green) (e), IB4 (green) (f) and Vimentin (red) (e, f) in myocardial tissues from KDM5B-KO or WT mice on Day 7 after MI surgery. Scale bar, 50 μm. Similar results were obtained from three independent experiments. g Q-PCR analysis of Vegfa, Cd31, Vegfr2, Nos3 and Vwf mRNA expression in KDM5B-deficient (KO) or WT cardiac fibroblasts stimulated with TGF-β (10 ng/ml) for 24 h (n = 4 per group). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01. Unpaired Student’s t test (a, g) was performed.