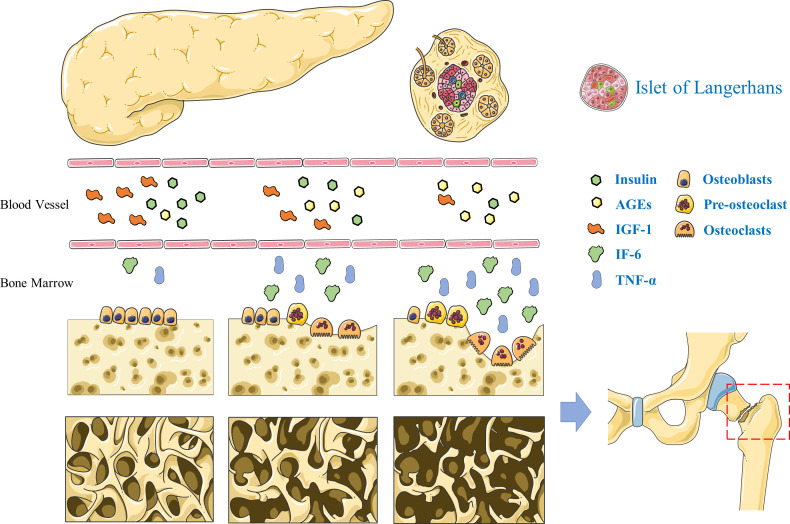
Figure 1.
Pathogenesis of diabetic bone disease. The deficiency of insulin and insulin-like growth factor-1 leads to decreased bone formation in T2DM. Advanced glycation end products inhibited osteoblasts differentiation. Interleukin-6 and tumor necrosis factor α can promote the proliferation and differentiation of osteoclast precursor cells into mature osteoclasts and accelerate the process of bone resorption.