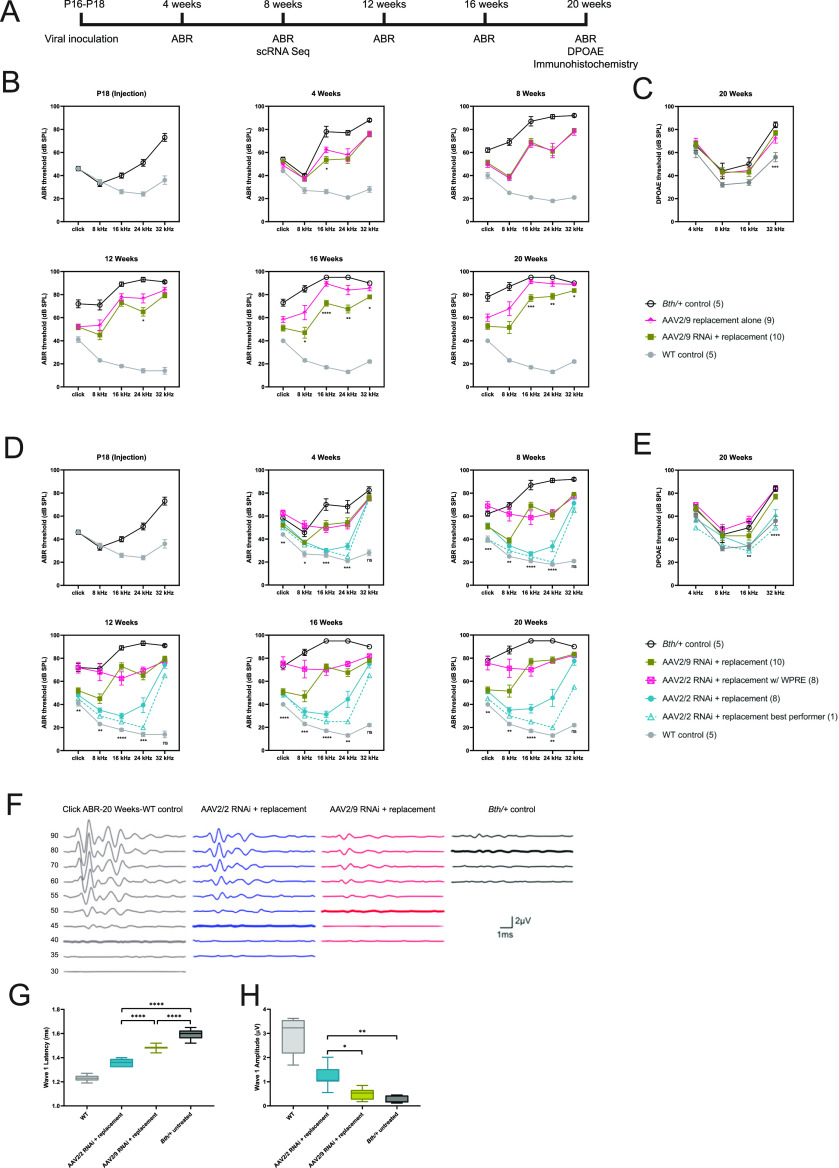
Figure 3. Allele-non-specific RNAi with engineered replacement durably improves auditory performance in Tmc1Bth/+ mice.
(A) After viral inoculation at P16–18, auditory brainstem responses (ABRs) were measured every 4 wk until 20 wk of age. DPOAE and immunohistochemistry were conducted at 20 wk. Hair cells were extracted for single-cell RNA-Seq at 8 wk. Statistical testing for ABR and DPOAE thresholds is reported in Tables S1–S4. (B) ABR thresholds recorded from 4 to 20 wk in Bth/+ mice treated with AAV2/9 gene replacement alone and AAV2/9 RNAi + gene replacement. (C) DPOAE thresholds recorded at 20 wk. (D) ABR thresholds recorded from 4 to 20 wk in Bth/+ mice treated with AAV2/9 RNAi + replacement, replacement, and AAV2/2 RNAi + AAV2/2 RNAi +replacement with WPRE. (E) DPOAE thresholds recorded at 20 wk. (F) Representative click ABR waveforms at 20 wk of age. (G, H) Wave 1 latency (G) and amplitude (H) at 90 dB SPL of WT control, AAV2/2 RNAi + replacement, AAV2/9 RNAi + replacement, and Bth/+ control were compared. Latency comparison: one-way ANOVA, P < 0.0001, and Tukey’s multiple comparisons test, P < 0.0001 for all between-group comparisons; amplitude comparison: Welch’s ANOVA, P < 0.0001, and Dunnett’s T3 multiple comparisons test: P = 0.003 for AAV2/2 RNAi + replacement versus Bth/+ control, P = 0.02 for AAV2/2 RNAi + replacement versus AAV2/9 RNAi + replacement, and P = 0.2 for AAV2/9 RNAi + replacement versus Bth/+ control. ****P < 0.0001; ***P < 0.001; **P < 0.01; and *P < 0.05. Data are means ± SEM. N mice per experimental condition are indicated in parentheses.