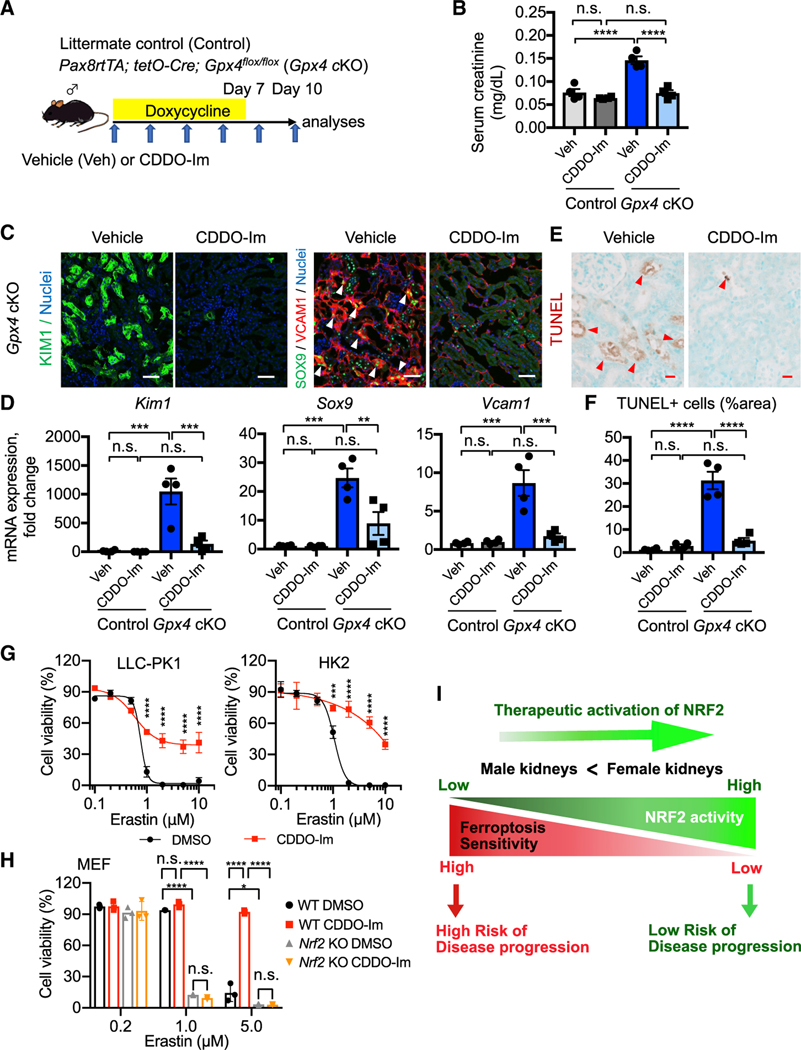
Figure 7. Pharmacological NRF2 activation prevents ferroptosis in Gpx4-deficient kidneys.
(A) Experimental workflow for testing NRF2 function in regulating ferroptotic stress and ferroptosis using Gpx4 cKO mice. Gpx4 cKO mice were administered either vehicle or CDDO-Im (NRF2 inducer) on alternate days. Doxycycline was given for 7 days, and mice were harvested on day 10.
(B) Serum creatinine levels in vehicle- versus CDDO-Im-treated Gpx4 cKO mice. n = 4.
(C) Immunostaining for KIM1, SOX9, and VCAM1. See Figure S10D for KIM1 quantification. Representative images are shown. Arrowheads, SOX9+/VCAM1+ cells. n = 4.
(D) Real-time PCR analyses of indicated gene expression. n = 4.
(E and F) TUNEL staining for evaluating cell death. Quantification of TUNEL+ area is shown in (F). n = 4. Arrowheads, TUNEL+ cells.
(G) Cellular viability assays using pig (LLC-PK1) and human (HK2) proximal tubular cell lines.
(H) Cellular viability assays using wild-type (WT) and Nrf2 knockout mouse embryonic fibroblasts (MEFs). Erastin (system Xc− inhibitor) was used for inducing ferroptosis in these cells.
One-way ANOVA (B, D, and F) and two-way ANOVA (G and H) with post hoc multiple comparisons test. n.s., not significant. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001; ****p < 0.0001. Scale bars: 50 μm in (C) and 20 μm in (E). Data are represented as mean ± SEM in (B, D, and F) and mean ± SD in (G and H).
(I) Proposed model. NRF2 acts as a rheostat for modulating ferroptosis sensitivity of proximal tubular cells.