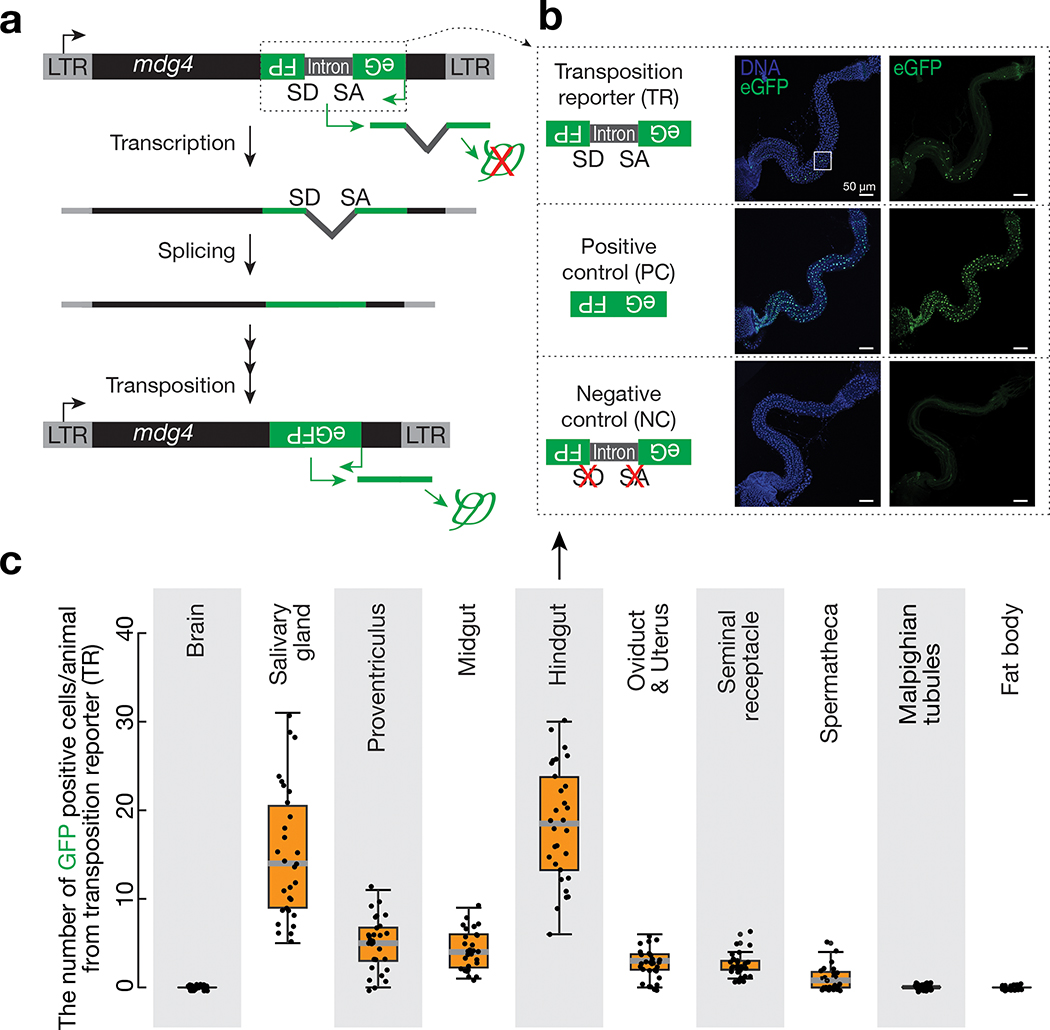
Fig. 1 |. Monitoring mdg4 mobilization in somatic cells via a transposition reporter.
a, Schematic design of an eGFP reporter to monitor mdg4 mobilization. The eGFP reporter is inserted in the non-coding sequence of mdg4 in the antisense orientation. eGFP is disrupted by an intron, which is in the same direction as mdg4 but opposite direction as eGFP. The intron cannot be spliced during eGFP transcription. mdg4 mobilization, which generates a new copy of the transgene without the disrupting intron, results in eGFP expression. b, mdg4 transposition reporter produces eGFP in hindgut cells in 2–4-day-old adult flies. An intronless construct is used as a positive control to test the potential sensitivity. A construct with mutated splicing acceptor and donor sites serves as a negative control. The boxed region is displayed in Extended Data Figure 1d to show eGFP signals are from nuclei (eGFP has nuclear localization signal sequences). c, The box plot shows the number of eGFP positive cells from mdg4 transposition reporter among different tissues from 2–4-day-old adult flies (N = 30). Box plots report the minimum, maximum, median, and interquartile ranges of the data.