Fig. 9.
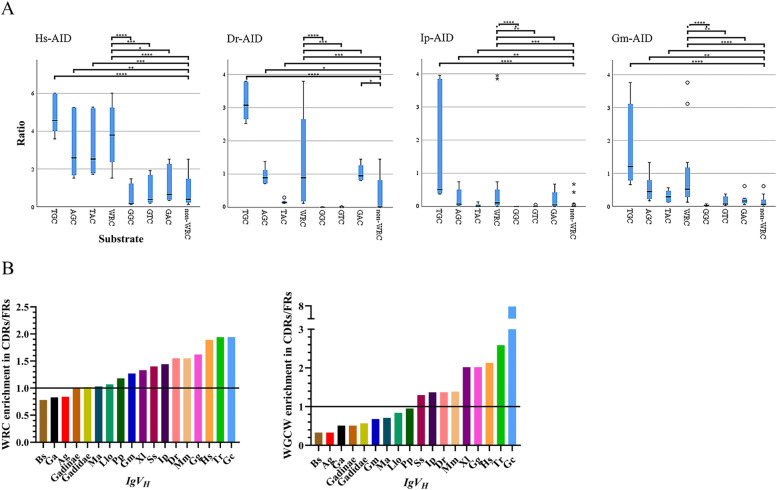
Co-evolution of the catalytic efficiency of AID with WRC enrichment in the Ig variable gene sequences in Gadidae species. A Substrate sequence preference of Gm-AID compared to that of other AID orthologs as determined by the statistical analyses of the difference observed between substrates of varying sequences’ relative deamination efficiency by various AID orthologs in the alkaline cleavage assay such as shown in Fig. 3B. The statistical difference between AID orthologs were calculated using the independent samples Rruskal-Wallis test. The null hypothesis was considered as the distribution is the same between each pair of samples (n = 6; *: p < 0.05; **: p < 0.01; ***: p < 0.005; ****: p < 0.001). Abbreviations: Gm-AID: Atlantic cod AID; Dr-AID: zebrafish AID; Ip-AID: channel catfish AID; Hs-AID: human AID. To assess the co-evolution of AID activity with IgVH sequences in Gadidae species, enrichment of B WRC motifs (AID hotspots on both strands) and C WGCW motifs (overlapping AID hotspots on two strands) in CDRs of Gadidae species were compared to that of several other vertebrate species. The number of WRC/GYW or WGCW motifs were counted and normalized to the number of analyzed nucleotides. For each species, the average normalized value for CDR1 and CDR2 was divided by the average value of this number for FR1, 2, and 3. Abbreviations: Bs: B. saida; Ga: G. argenteus; Ag: A. glacialis; Ma: M. aeglefinus; Llo: L. lota; Pp: P. phycis; Gm: G. morhua; Dr: D. rerio; Ss: S. salar; Ip: I. punctatus; Tr: T. rubripes; Gc: G. cirratum; Xl: X. laevis; Gg: G. gallus; Mm: M. musculus; Hs: H. sapiens