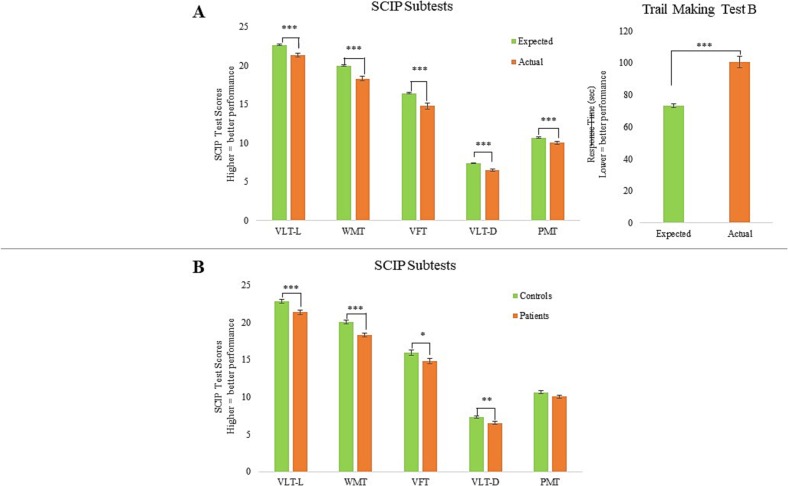
Fig. 2.
Pattern of cognitive impairments in patients (n = 194) on average 7 months (SD = 4) months after COVID-19 in comparison (A) with normative scores adjusted for age, sex and education estimated with regression models and (B) with an age-, sex- and education-matched healthy control group (n = 150). Most pronounced impairments were seen in working memory (WMT) and executive function (TMT-B). Graphs represent the mean and error bars the standard error of the mean. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001.