FIGURE 4.
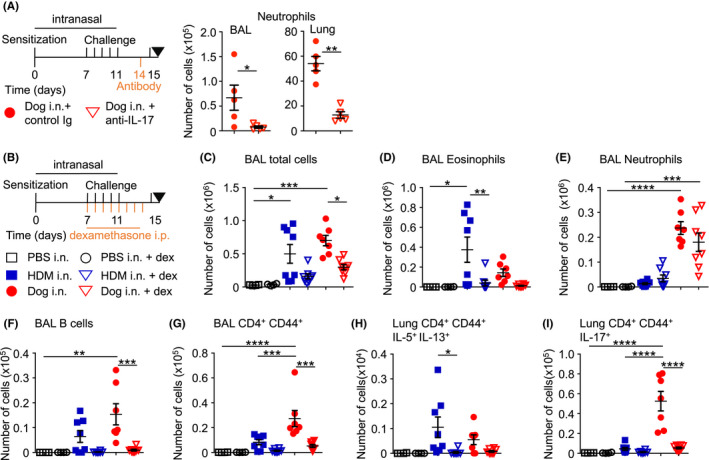
Dexamethasone reduces airway inflammation after administration of dog allergen extracts. (A) Regimen of intranasal allergen challenge with intraperitoneal anti‐IL‐17 or control Ig (500 μg each) administration. Levels of airway and lung tissue neutrophils are shown, n = 5 mice in each group. (B) Regimen of intranasal allergen challenge with intraperitoneal dexamethasone/vehicle control administration: PBS i.n. vehicle i.p. n = 4 (open square), PBS i.n. dexamethasone i.p. n = 4 (open circle), HDM i.n. vehicle i.p. n = 8 (blue square), HDM i.n. dexamethasone i.p. n = 8 (open blue triangle), dog i.n. vehicle i.p. n = 8 (red circle), or dog i.n. dexamethasone i.p. n = 8 (open red triangle). (C) Total number of cells in the BAL. (D) Number of eosinophils in the BAL. (E) Number of neutrophils in the BAL. (F) Number of B cells in the BAL. (G) Number of effector T helper cells in the BAL. (H) Number of IL‐5+ IL‐13+ T helper cells in the lung. (I) Number of IL‐17+ T helper cells. One‐way ANOVA with Bonferroni's post‐test was performed to adjust for multiple comparisons. *p < .05, p < .01, ***p < .001, ****p < .0001
