FIGURE 1.
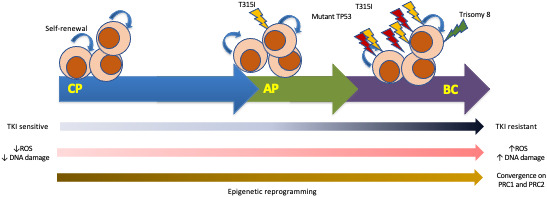
Clonal evolution in CML. The schematic diagram proposes a model for clonal evolution in CML. Acquisition of BCR‐ABL1 within a stem/progenitor cell results in an increase in ROS, genomic instability and epigenetic reprogramming with convergence on PRC1 and PRC2 complexes. 21 , 22 , 23 AP‐CML may develop when additional mutations, e.g. T315I, occur and treatment resistance ensues. Further progression to BP occurs when leukaemic progenitor cells acquire self‐renewal potential, which is combined with worsening genomic instability leading to acquisition of further genetic abnormalities, e.g. TP53 mutation, trisomy 8 and differentiation block. AP, accelerated phase; BP, blast phase; CML, chronic myeloid leukaemia; CP, chronic phase; ROS, reactive oxygen species; TKI, tyrosine kinase inhibitor.
