Fig. 1.
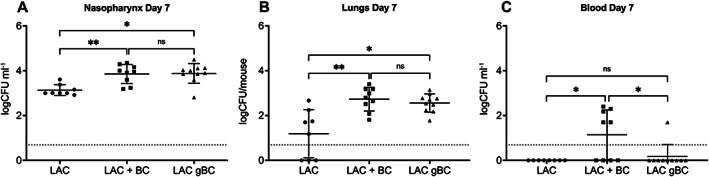
Exposure of S. aureus to BC results in increased respiratory tract colonization in mice. Female CD1 mice were intranasally inoculated with 15 μl containing 107 S. aureus LAC (−BC), 107 LAC with 105 μg BC (+BC) or 107 CFU LAC pre‐grown in the presence of 100 μg ml−1 BC (gBC). After 7 days, bacteria were recovered from the nasopharynx (A), lungs (B) and blood (C) and plated to determine the bacterial CFUs. No mice showed any clinical signs of infection. Data are presented as logCFU ml−1 for nasopharyngeal washes and blood, and logCFU/mouse for lungs. The dotted line marks the limit of detection. Data were analysed using a Kruskal–Wallis test with Dunn's multiple comparison (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01).
