FIGURE 2.
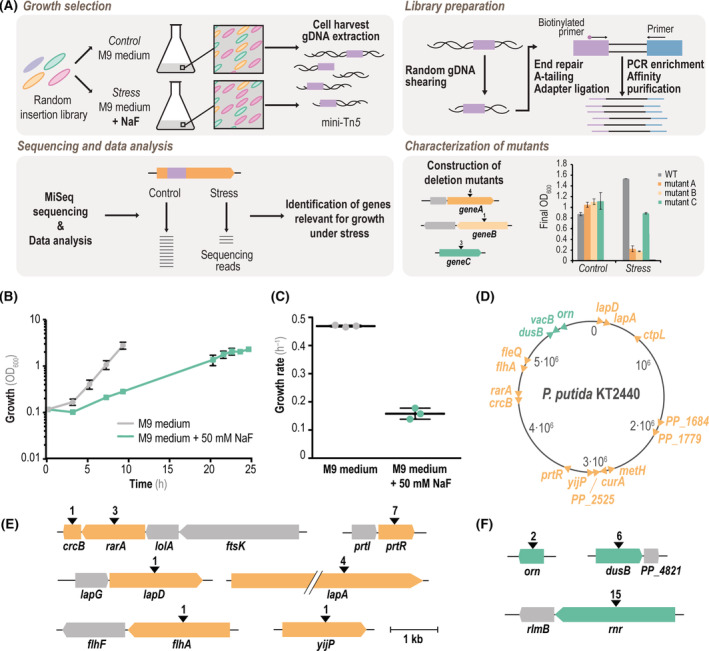
Tn‐Seq‐guided identification of genes relevant for bacterial growth in the presence of mineral F−. (A) Workflow of the experimental procedure for Tn‐Seq experiments. A Tn5 insertion library (transposons depicted as purple boxes) was used in growth assays under control and stress (+NaF) conditions in order to assess differential growth of Tn5‐insertion mutants of wild‐type (WT) P. putida KT2440. After harvesting the bacterial biomass, genome DNA (gDNA) was extracted and processed by mechanical shearing, A‐tailing and ligation of adapters (blue boxes), followed by PCR enrichment as indicated in Experimental procedures. The resulting library was subsequently analysed by next‐generation sequencing (MiSeq), and the number of readings under different experimental conditions were compared to assess the differential abundance of individual insertions. Genes relevant for growth of strain KT2440 in the presence of NaF were identified, and the deletion mutants in the corresponding genes (listed in Table 1) were constructed and characterized as described in the text. (B) Growth of the library of Tn5‐insertion mutants of P. putida KT2440 in M9 minimal medium containing 5 g L−1 glucose as the only carbon source (grey) and the same medium supplemented with 50 mM NaF (green). Growth was estimated as the optical density measured at 600 nm (OD600), and the biomass was harvested for gDNA extraction and processing at the end‐point (i.e. no further changes in OD600) for each culture condition. (C) Specific growth rates of P. putida KT2440 grown under control conditions (M9 minimal medium containing 5 g L−1 glucose, grey) and stress conditions (+50 mM NaF, green). (D) Physical map of the genome of strain KT2440 identifying the insertion sites in relevant genes found in the Tn‐Seq assay. Insertions with a log2(fold change, FC) < −2 (genes relevant for survival in the presence of NaF) are shown in orange. Insertions with a log2(FC) > 2 (mutations positively affecting growth with NaF) are indicated in green. (E) Genetic context of genes identified to be important for bacterial growth in the presence of 50 mM NaF (orange) by Tn‐Seq. The number of insertions is indicated with black arrowheads, and genes highlighted in grey represent the genetic context of predicted operons. (F) Same as panel (E), but showing genes with positively affecting insertions (green) and their genetic context. The same scale is used in panels (E) and (F)
