Figure 2.
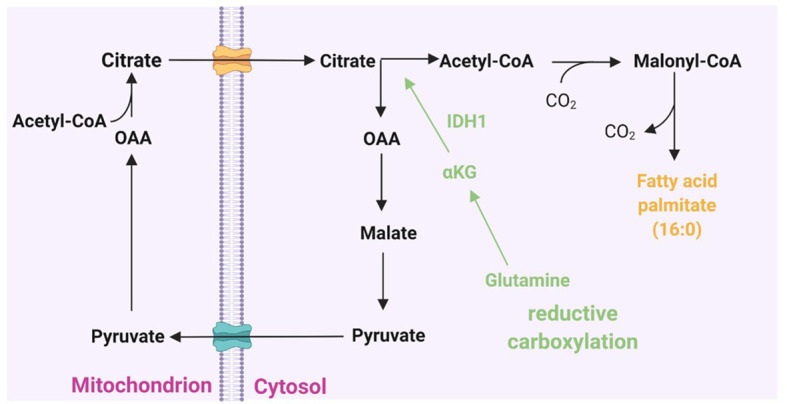
Cytoplasmic citrate pool and fatty acid synthesis. Acetyl-CoA couples with oxaloacetate (OAA) to form citrate at the beginning of the citric acid cycle. Citrate can then shuttle across the mitochondrial membrane to the cytoplasmic citrate pool. In the cytosol, citrate lyase splits citrate back into acetyl-CoA and OAA. The latter can then return to the mitochondrion. Acetyl-CoA is activated in the cytoplasm for incorporation into fatty acids by acetyl-CoA carboxylase to form malonyl-CoA and then to de novo fatty acid synthesis. Glutamine-derived α-ketoglutarate (α-KG) can add to the cytoplasmic citrate pool via reductive carboxylation to provide an alternative source of lipid synthesis.
