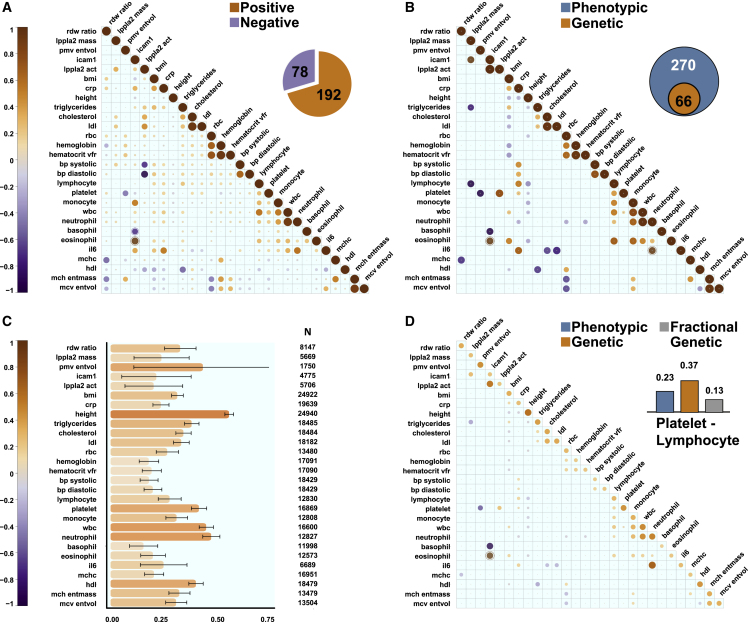
Figure 2.
Genetic basis of observed phenotypic correlations between phenotypes in the combined TOPMed dataset
Correlation matrices where each column and row represent one of the 28 phenotypes in the TOPMed dataset (n = 33,959), and the intersection is the estimated correlation magnitude. Size and color of circle indicates the correlation strength: dark orange, positive; dark purple, negative correlation.
(A) Phenotypic correlations between the phenotypes. Inset: number of positive and negative correlated phenotype pairs with p < 0.05.
(B) Estimated genetic correlations () (shown only for phenotype pairs with p < 0.05 between the phenotypes). Inset: number of phenotype pairs with both phenotypic and genetic correlations with p < 0.05 in this dataset.
(C) Estimated heritabilities for the studied phenotypes.
(D) Fractional genetic correlations ( between the phenotypes (shown only for phenotype pairs with p < 0.05). Inset: example of phenotypic and genetic correlation where the absolute value of the genetic correlation is larger than that of the phenotypic correlation which complicates interpretability.