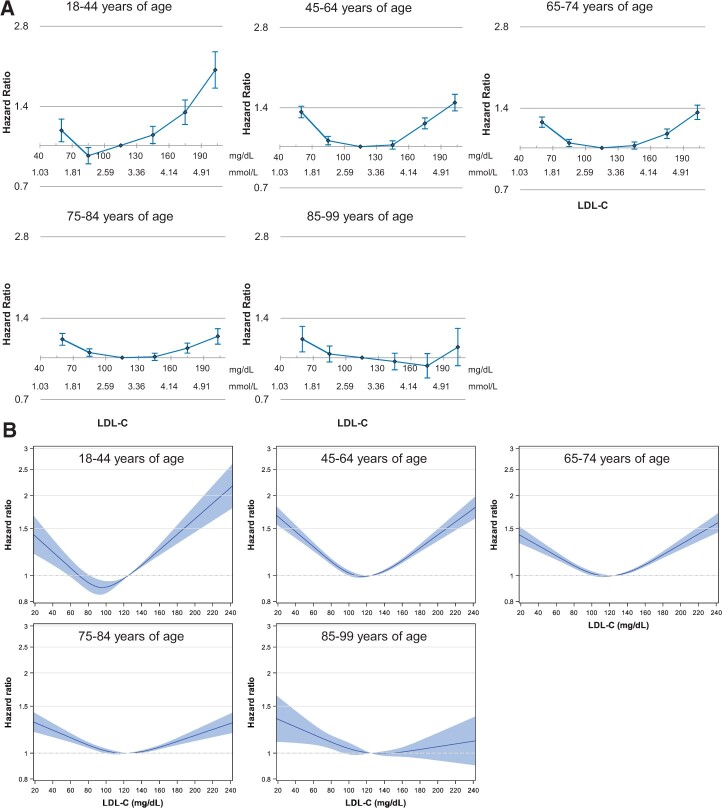
Figure 2.
Hazard ratios of LDL-C for CVD mortality according to age. (A) LDL-C categories [mg/dL: <70, 70–99, 100–129 (reference), 130–159, 160–189, ≥190]. The midpoint was used as a representative value of each LDL-C category, except both ends (45 and 205) for which the median was used. (B) Restricted cubic splines of LDL-C with four knots (5th, 35th, 65th and 95th percentiles) and 125 mg/dL as a reference were used. Hazard ratios and 95% CIs were calculated using Cox proportional-hazards models with adjustment for age at baseline, sex, smoking status, alcohol consumption frequency, physical activity, household income, systolic blood pressure, fasting glucose, body mass index, triglyceride and high-density lipoprotein cholesterol. CVD, cardiovascular disease; LDL-C, low density lipoprotein cholesterol. To convert LDL-C from mg/dL to mmol/L, multiply by 0.02586