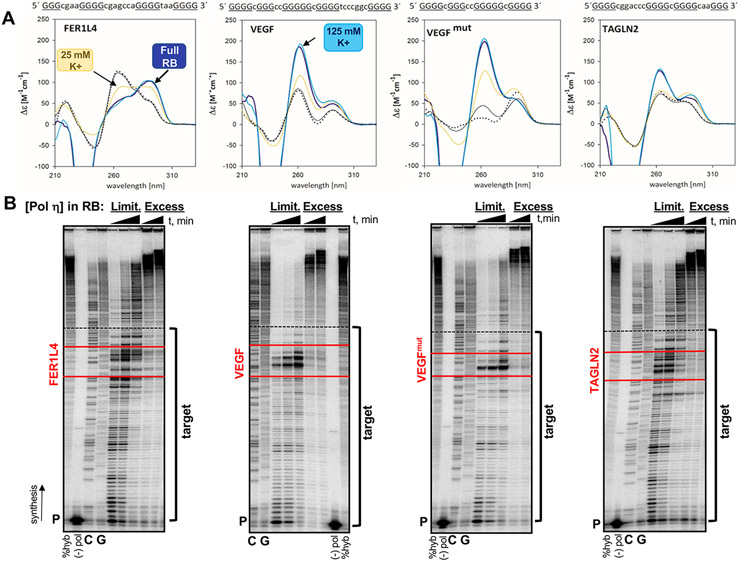
Figure 1. FER1L4, VEGF and TAGLN2 motifs form G4 secondary structures.
(A) Circular dichroism spectra were generated for each G4 motif in the following conditions: yellow line, 25 mM K+ phosphate (pH 7.2) buffer; dark blue line, full polymerase reaction buffer (RB, 25 mM K+-phosphate, 5 mM MgCl2, 5 mM DTT, 100 ug/mL BSA); teal line, full RB plus 100 mM KCl (“125 mM K+”); solid black line, before denaturation in 1mM NaPO4 low ionic salt; dotted black line, after denaturation (5 minutes at 90°C). FER1L4 , antiparallel structure; VEGF and VEGFmut , parallel structures; TAGLN2, hybrid (3+1) structure. Sequence of each G4 motif is given with G-tract, uppercase and underlined; Loop, lowercase. (B) Representative gel images of human pol η pausing analyses. Reactions were performed in the full RB under limiting (Limit) enzyme (1-2 pmol) or Excess enzyme (7.5 pmol) conditions. Triangle indicates time (30, 60, and 120 min limiting; 60 and 120 min excess ). Target indicates template sequences for the polymerase gap-filling assay. Red lines border the G4 motifs. The primer (P) includes the StuI site at HSV-tk position 180 (3’ end of Target); dashed black line indicates the MluI site at HSV-tk position 83 (5’ end of target). %Hyb, total amount of productively hybridized primer for DNA synthesis; (−) pol, reactions without polymerase; GC, sequencing ladder.