Figure 1 – Synthetic guide piRNAs silence endogenous genes.
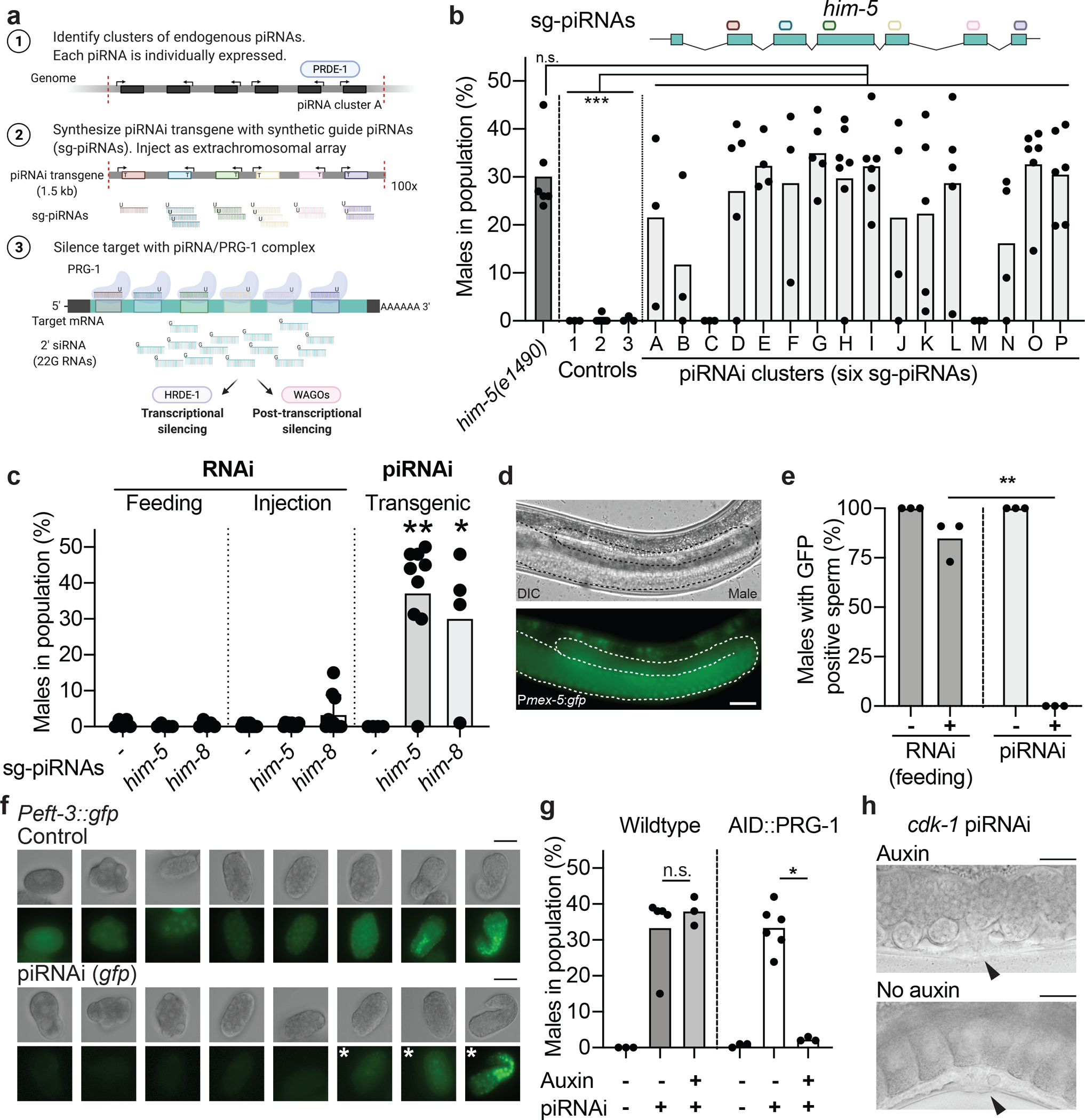
a. Schematic overview of piRNA-mediated RNA interference (piRNAi). Synthetic guide piRNAs (sg-piRNAs, 21 nt) are expressed from semi-stable extra-chromosomal arrays and silence target mRNAs via transcriptional and post-transcriptional mechanisms.
b. Silencing the endogenous him-5 gene with six sg-piRNAs expressed using 16 different recoded piRNA clusters (A to P) results in increased male frequency. The schematic above the him-5 locus indicates the location of antisense sg-piRNAs. Controls = him-5(e1490) mutant animals and negative controls: “1” = unmodified piRNA clusterA, “2” = him-5 sense sg-piRNAs, “3” = six sg-piRNAs targeting gfp. Kruskal-Wallis ANOVA P < 0.0001, Dunn’s multiple comparison. *** P = <0.001 and n.s. P > 0.999.
c. Gene silencing of him-5 or him-8 by RNAi by feeding (left), injection of in vitro transcribed dsRNA (middle), or piRNAi (right, clusterE) in Pmex-5::gfp transgenic animals. Controls (“−”) = empty RNAi vector (pL4440), dsRNA targeting gfp, and piRNA clusterE with randomized sg-piRNAs, respectively. Mann-Whitney test, comparison between RNAi and piRNAi condition. ** P = 0.0060 and * P = 0.0397.
d. Male sperm expressing GFP from a Pmex-5::gfp transgene. The male germline is outlined with a white dotted line. 40x magnification. Scale bar = 25 um.
e. Quantification of GFP expression in male sperm by visual inspection after silencing with RNAi (left) and piRNAi (right). Two-tailed t-test with Welch’s correction, ** P = 0.0049.
f. sg-piRNAs targeting a ubiquitous gfp (Peft-3::gfp) silences fluorescence in the germline (not shown) and in embryos until approximately the 100-cell stage (visible GFP fluorescence indicated by white asterisks). Representative images from more than ten embryos imaged. Scale bar = 25 um.
g. Conditional piRNAi using an auxin-inducible degron (AID) at the endogenous prg-1 locus26. In the presence of auxin (“+”), PRG-1 is degraded. “−” = un-injected strain. Mann-Whitney test, * P = 0.0238, n.s. = not significant.
h. Conditional piRNA-mediated silencing of cdk-1 in AID::PRG-1 animals result in single-cell embryonic arrest when transgenic animals are shifted to plates with no auxin. Arrowhead indicates the vulva. Representative images from more than ten adult animals. Scale bar = 25 um.
Data are presented as mean values +/− SEM with each data point corresponding to an independently derived transgenic strain. Sample sizes (b) n = 6 (him-5), n = 3 (“1”), n = 7 (“2”), n = 3 (“3”), n = 3 (A), n = 3 (B), n = 3 (C), n = 5 (D), n = 4 (E), n = 3 (F), n = 5 (G), n = 7 (H), n = 6 (I), n = 4 (J), n = 5 (K), n = 5 (L), n = 3 (M), n = 4 (N), n = 6 (O), n = 6 (P) biologically independent transgenic animals, (c) Feeding: n = 5 (all conditions) biologically independent animals; Injection: n = 10 (all conditions) biologically independent animals; piRNAi: n = 4 (“−”), n = 9 (him-5), n = 4 (him-8) biologically independent transgenic animals, (e) RNAi: n = 3 (both conditions) biologically independent animals, piRNAi: n = 3 (both conditions) biologically independent transgenic animals, (g) Wildtype: n = 3 (“−/−”), n = 5 (“−/+”), n = 3 (“+/+”), AID::PRG-1: n = 3 (“−/−”), n = 6 (“−/+”), n = 3 (“+/+”) biologically independent transgenic animals.
