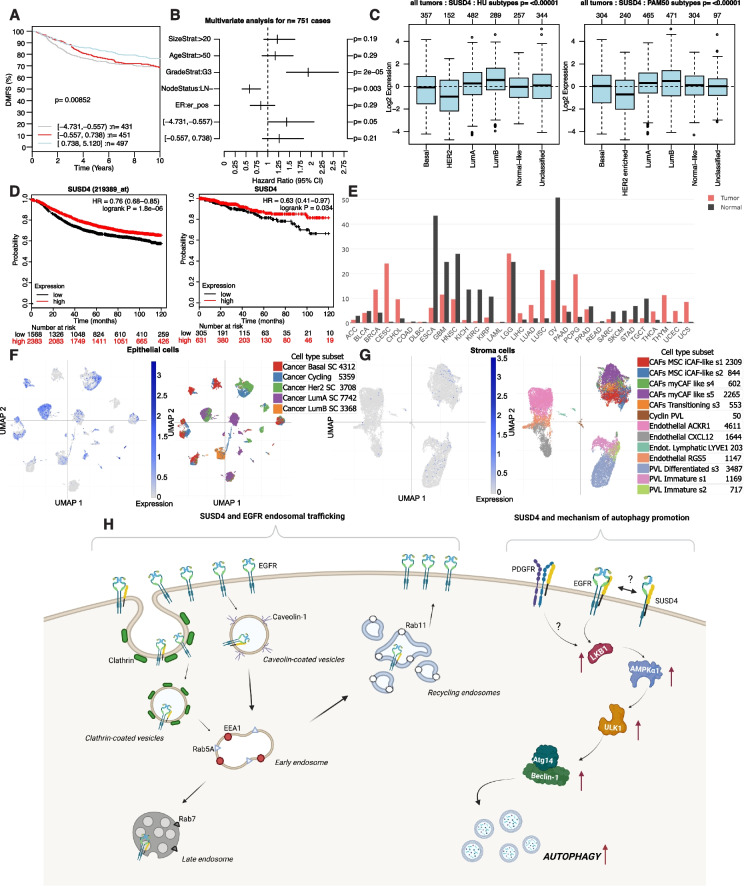
Fig. 7.
SUSD4 expression data in breast cancer. Expression data for SUSD4 in breast cancer patients obtained from the GOBO database. A Kaplan-Meier survival analysis displaying distant metastasis free survival of patients with high expression of SUSD4 (log2 expression 0.738, 5.120), intermediate expression (log2 expression − 0.557, 0.738) or low expression (log2 expression − 4.731, − 0.557). B Multivariate analysis indicating low SUSD4-expression as an independent prognostic factor for survival. C Expression of SUSD4 in breast cancer subsets. D Kaplan Meier survival analysis showing relapse free survival for breast cancer patients with high or low expression of SUSD4 assessed by microarray analysis (left, n = 3951) or mRNA sequencing (right, n = 936). E Data obtained from the Gene Expression Profiling Interactive Analysis database showing the expression of SUSD4 in tumorous tissues compared to paired healthy tissues. Data obtained from the Broad Institute Single Cell Portal showing the expression of SUSD4 in epithelial cells of different breast cancer subtypes (F) and in different stromal cells (G). Figure showing a proposed effect of SUSD4 expression in breast cancer cells and its relationship to EGFR and autophagy. In brief, SUSD4 binds to EGFR and initiates autophagy in an EGFR phosphorylation-independent manner. Autophagy initiation is affected by the phosphorylation of SUSD4 at the LSPY site. In addition, CCP1 and 2 in the extracellular part of SUSD4 play a role in autophagy initiation. Onwards, the downstream pathway of LKB1, AMPKa1, ULK1, Atg14 and Beclin-1 is activated, leading to increased autophagic flux. Finally, SUSD4 colocalizes with different endosomal vesicles. SUSD4 and EGFR are highly colocalized with Rab11-positive recycling endosomes indicating a potential effect of SUSD4 on EGFR recycling to the plasma membrane, (H) created with BioRender.com