Figure 1.
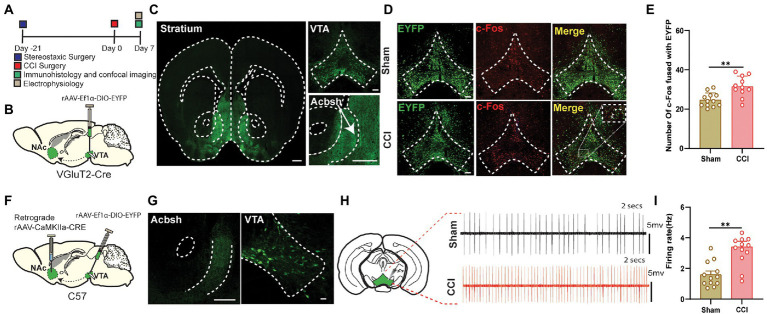
The neuropathic pain can induce hyperactivity in the VTA Glutamate neurons projecting to NAc. (A) Experimental timeline. For the immunohistological expression, the DIO-EYFP viral vector was injected in the VTA brain region and VGluT2-Cre mice were given 21 days for the expression of the virus before the CCI surgery. The c-Fos labeling was performed on day 7 after the sham or CCI surgery (unilateral sciatic nerve ligation) in mice. (B) Schematic illustration depicting viral constructs and experimental surgery in VGluT2-Cre mice. (C) Confocal image of VTA somatic expression of DIO-EYFP (Scale bar = 200 μm) and VTA VGluT2 fibers projecting to NAc (Scale bar = 500 μm and Scale bar = 200 μm); these fibers are highly concentrated in NAc shell. (D) Representative confocal images of VTA glutamatergic somatic cell bodies infected by DIO-EYFP and stained with c-Fos of both sham (without nerve ligation) and CCI mice (unilateral sciatic nerve ligation); these images were demarcated as DIO-EYFP only, c-Fos labeled only and merged image of DIO-EYFP infected somatic bodies coupled with c-Fos protein. Scale bar = 200 μm. (E) Quantitative data regarding the comparison between c-Fos protein expression coupled with DIO-EYFP infected glutamatergic somatic cell bodies of VTA brain region in the sham group vs. CCI group of the VGluT2-Cre mice (n = 12 slices/group from 3, 3 mice; **p < 0.01, unpaired-sample t-test). (F) Experimental timeline. For the immunohistological expression, retrograde CaMKIIa-CRE viral vector was injected in the NAc brain region, DIO-EYFP viral vector was injected in the VTA brain region, and wild-type mice were given 21 days for the expression of the virus before the CCI surgery. The electrophysiological recordings for the firing rate were done on day 7 after the sham or CCI surgery (unilateral sciatic nerve ligation) in wild-type mice. (G) Confocal images showing virus expression in the VTA somatic body and NAc axon terminals in the brain region of wild-type mice infected by the viral vector of CaMKIIa-CRE and DIO-EYFP for the labeling of the glutamatergic projections. Scale bar = 200 μm and Scale bar = 100 μm. (H) Traces of firing activity of the glutamatergic somatic bodies of VTA (with axonal projections to NAc) in wild-type mice. (I) Quantitative data regarding the firing activity of glutamate neurons in VTA (with axonal projections to NAc) of sham and CCI groups (24 neurons from 6, 6 mice, **p < 0.01, unpaired-sample t-test).