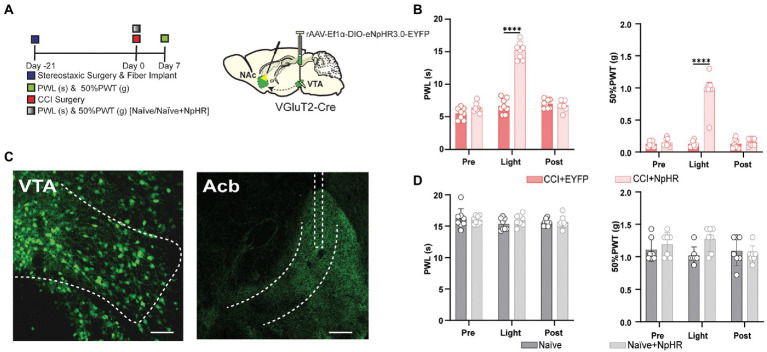
Figure 3.
Inhibition of the glutamatergic neurons projected from VTA to NAc has relieved neuropathic pain in VGluT2-Cre mice. (A) Experimental timeline. Schematic illustration depicting viral constructs. For the terminal stimulation, DIO-NpHR-EYFP was injected in the VTA, the optical fiber was planted at the NAc in VGluT2-Cre mice, and mice were given 21 days for the expression of the virus before the CCI surgery or before PWLs and 50% PWTs measurement in naïve mice. PWLs and 50% PWTs of the hind paws were assessed on day 7 after CCI surgery in VGluT2-Cre mice. (B) The quantitative comparison of PWLs and 50% PWTs between the two groups (with and without light stimulation). Statistics showing that CCI + NpHR group exhibited a significant increase in PWLs during the terminal light stimulation period [Light phase] compared with the CCI + EYFP group (n = 8, 8 mice; ****p < 0.0001), 50% PWTs of CCI + NpHR group were also significantly increased during the terminal light stimulation [Light phase] compared with the CCI + EYFP group (n = 8, 8 mice; ***p < 0.0001) in VGluT2-Cre mice. (C) Confocal images showing virus expression in the somatic bodies of VTA and terminal projection in NAc brain region of the VGluT2-Cre mice. Scale bar = 200 μm and scale bar = 200 μm. (D) The comparison of PWLs and 50% PWTs between the two groups of the naïve mice (with and without light stimulation), Statistics showing Naïve + NpHR group exhibited no significant difference in PWLs and 50% PWTs compared with the Naïve group (n = 7, 7 mice; p > 0.05) of the VGluT2-Cre mice (All the readings were measured during 3 consecutive periods and the comparisons were performed by the two-way ANOVA test followed by Bonferroni post-test).