Figure 7. Fos/AP‐1 signaling activation was associated with clinical CAD/MI risk and heart failure.
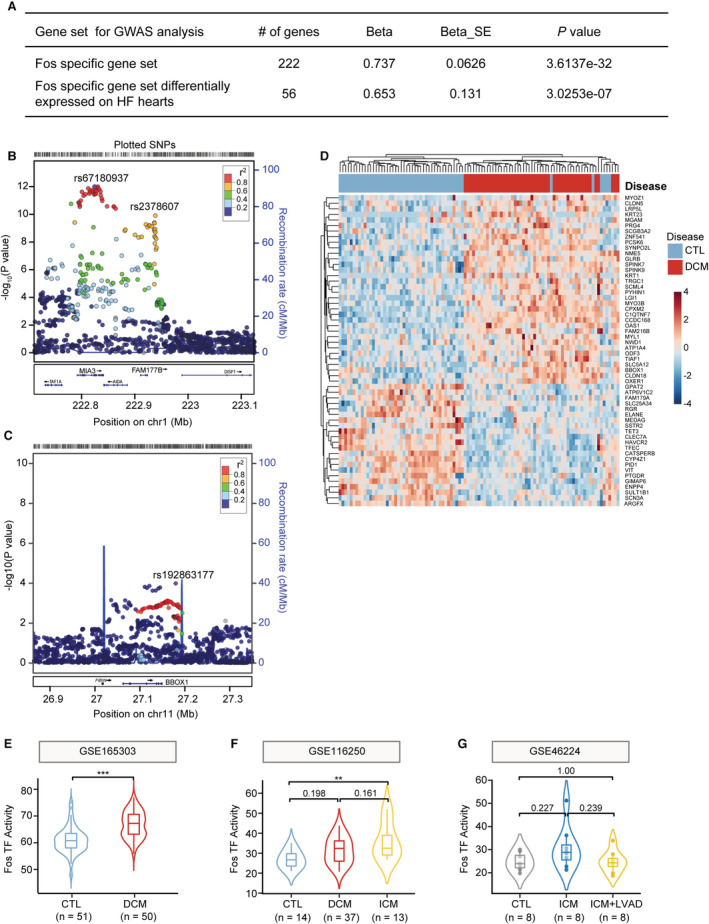
A, Gene‐set based analysis of CAD/MI risk signaling in CARDIOGRAMPLUSC4D genome‐wide association meta‐analysis study (GWAS). Fos/AP‐1 target genes (222 genes), and Fos/AP‐1 target genes that were differentially expressed in patients with heart failure in RNA‐seq data set (56 genes/222 genes, GSE165303) were used as queried gene lists for magma analysis. B and C, Regional association plots showing CAD/MI risk‐loci. Fos/AP‐1 target genes, FAM177B (B) and BBOX1 (C) were identified as potential risk loci. Linkage disequilibrium (r 2) was calculated based on the combined 1000 genomes. D, Reanalyzing RNA‐seq data (GSE165303) of dilated cardiomyopathy (DCM) and control patients (CTL) to determine the dysregulated expression of Fos/AP‐1 signaling in heart failure. E through G, Using 222 Fos/AP‐1 target genes, the Fos/AP‐1 activity was determined in RNA‐seq data sets of control and DCM patients (E, GSE165303, n=51, 50 in CTL and DCM, respectively; Student's t tests), or control, DCM, and ischemic cardiomyopathy (ICM) patients (F, GSE116250, n=14, 37, 13, respectively; 1‐way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni test), or the normal, patients with ICM before and after left ventricular assist device (LVAD) treatment (G, GSE46224, n=8 for each group; 1‐way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni test). AP‐1 indicates activator protein 1; CAD, coronary atherosclerosis diseases; MI, myocardial infarction; SNP, single nucleotide polymorphism; and TF, transcriptional regulon.
