Figure 5.
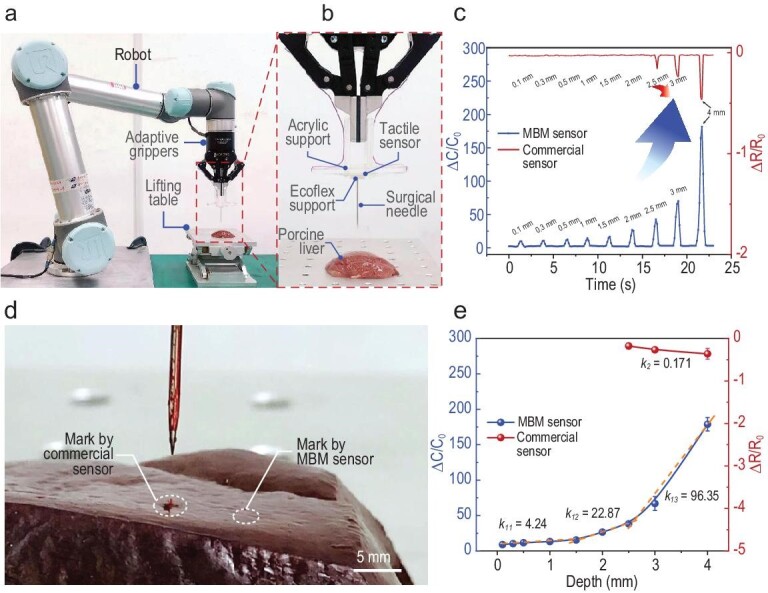
Monitoring of needle insertion operations by a robotic manipulator. (a) The experimental set-up. (b) Zoomed-in view of a sensor unit mounted on the manipulator for needle insertion monitoring. (c) Real-time monitoring of capacitance variations of the sensor installed at the bottom of the needle, and comparisons with commercial sensors. Penetration distances under 2.5 mm cannot be detected by the commercial sensor. (d) The penetration marks by the needle when the commercial sensor and MBM sensor just identify the contact between the needle and tissue. During the experiment, the needle moved towards the tissue until a noticeable change in 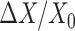 (resistance/capacitance) occurred, followed by the retreat of the needle. (e) Sensitivity, with regard to measuring penetration depth, of the MBM sensor and the commercial sensor.
(resistance/capacitance) occurred, followed by the retreat of the needle. (e) Sensitivity, with regard to measuring penetration depth, of the MBM sensor and the commercial sensor.
