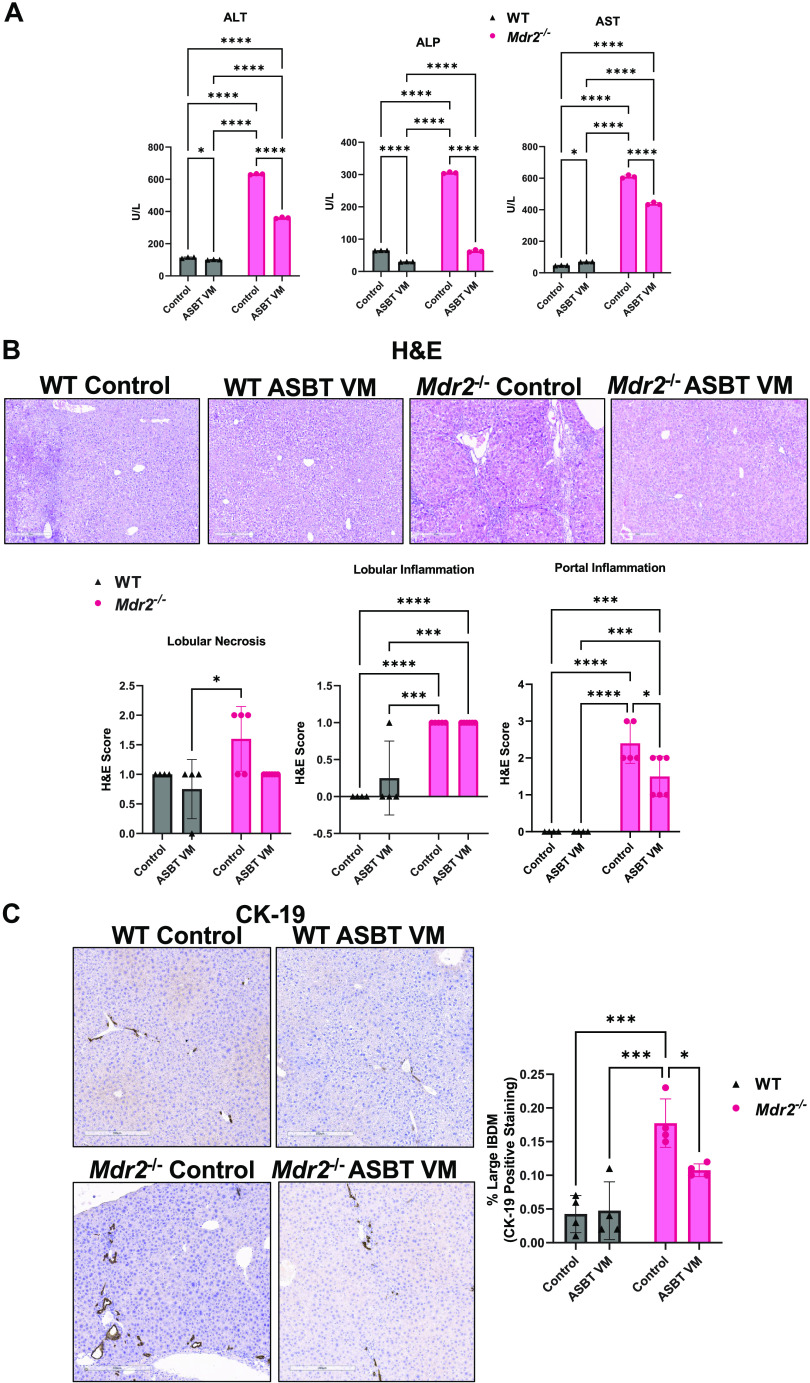
Figure 1.
Apical sodium bile acid (BA) transporter (ASBT) Vivo-Morpholino (VM) treatment reduces hepatic damage and large intrahepatic bile duct mass (IBDM) in multidrug-resistant 2 knockout (Mdr2−/−) mice. Alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and alkaline phosphatase (ALP) levels increased in Mdr2−/− Control mice compared with wild-type (WT) Control mice and were significantly decreased in both WT and Mdr2−/− mice treated with ASBT VM (A). Aspartate aminotransferase (AST) serum levels significantly increased in WT ASBT VM and Mdr2−/− Control mice but were reduced in Mdr2−/− mice after ASBT VM treatment (A). There was increased portal inflammation in Mdr2−/− mice treated with Control that was significantly reduced after ASBT VM treatment, and no differences in lobular inflammation were found between WT or Mdr2−/− mice treated with Control or ASBT VM (B). Large IBDM increased in Mdr2−/− Control mice compared with WT mice. ASBT VM reduced large IBDM in Mdr2−/− mice but had no effect in WT mice (C). Serum from 7–10 mice was combined and run in triplicates. The data are presented as mean ± SD of our technical replicates for serum chemistry. Data are presented as mean ± SD of whole tissue scanning for cytokeratin-19 (CK-19) and hematoxylin and eosin Y (H&E) analysis from 4 or 5 slides containing liver samples from 7 to 10 mice per group. Representative images are presented as ×10. *P < 0.05, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001.