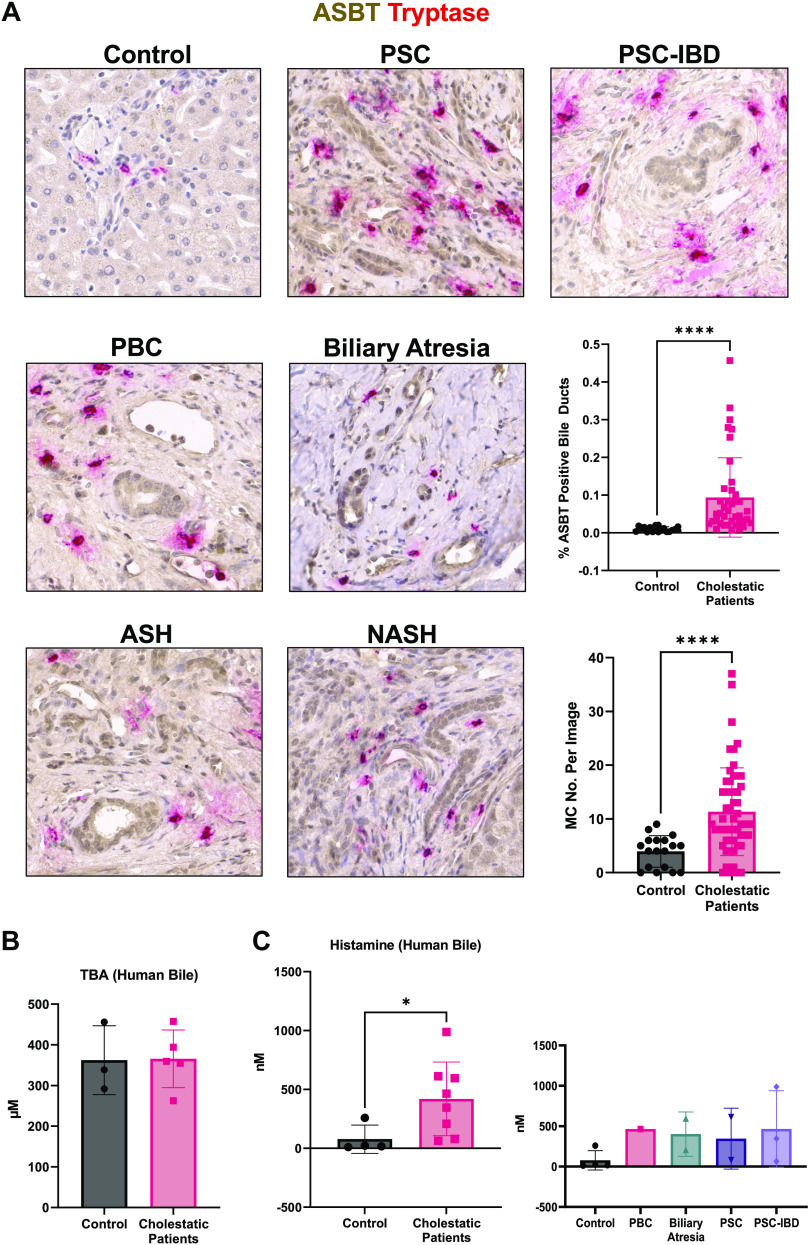
Figure 6.
Biliary apical sodium bile acid (BA) transporter (ASBT) and mast cell (MC) presence increase in patients with liver disease. Patients with primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC) or PSC with irritable bowel disease (IBD) have significant (assessed by semiquantification) increased biliary ASBT expression (brown) accompanied by significant elevated MC number (tryptase, red) (A) compared with nondiseased control patients. We also found that cholestatic patients [primary biliary cholangitis (PBC), biliary atresia] and patients with fatty liver diseases [alcoholic steatohepatitis (ASH), nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH)] display ASBT-positive bile ducts (brown) accompanied by MC presence (tryptase, red) compared with control subjects (A). Bile total bile acids (TBA) (B) were unchanged whereas histamine levels (C) increased in cholestatic patients compared with nondiseased control patients. Representative images are presented at ×40. Data are presented as mean ± SD of 3 experiments per patient for TBA and histamine enzyme immunoassay (EIA) from 7 cholestatic patients and 5 control patients and n = 5 nonoverlapping images for ASBT and MC quantification. *P < 0.05, ****P < 0.0001.