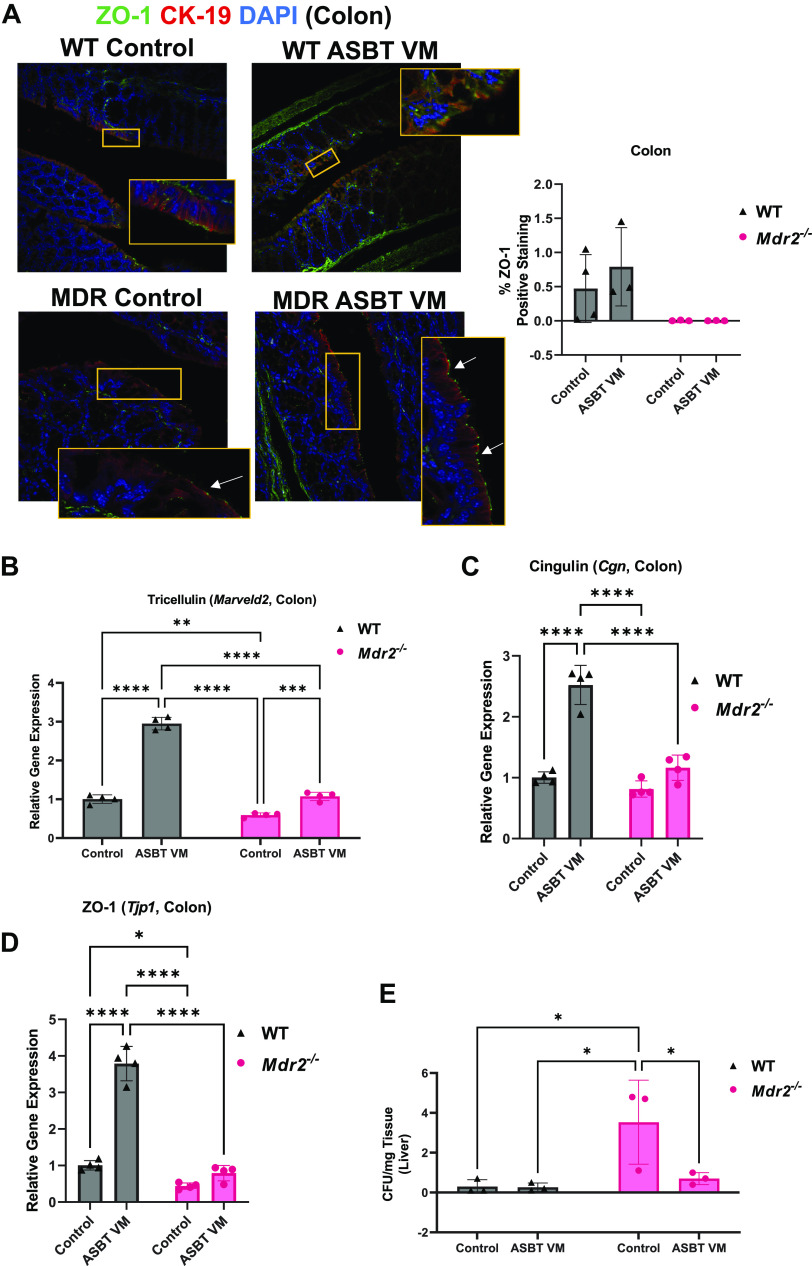
Figure 8.
Apical sodium bile acid (BA) transporter (ASBT) Vivo-Morpholino (VM) treatment reduces gut barrier integrity and bacterial translocation. Intestinal tight junction protein zonula occludens-1 (ZO-1) immunofluorescence and semiquantification was unchanged between wild-type (WT) and multidrug-resistant 2 knockout (Mdr2−/−) groups treated with either Control or ASBT VM (A). In the ileum, tight junction tricellulin expression decreased in Mdr2−/− control mice compared with WT but was increased in both WT and Mdr2−/− ASBT VM-treated mice compared with respective controls (B). Similarly, Mdr2−/− Control mice displayed decreased cingulin and ZO-1 expression compared with WT mice, whereas ASBT VM increased cingulin and ZO-1 expression in WT mice but they were unchanged in Mdr2−/− mice (C and D). Hepatic bacterial translocation was increased in hepatic tissue lysate of Mdr2−/− Control compared with WT mice but was reduced in Mdr2−/− mice treated with ASBT VM compared with Control-treated mice (E). Representative images presented at ×40 magnification; white arrows denote ZO-1-positive area. Data are presented as mean ± SD of 3 experiments for colony-forming units (CFU) from 3 mice per group. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001.