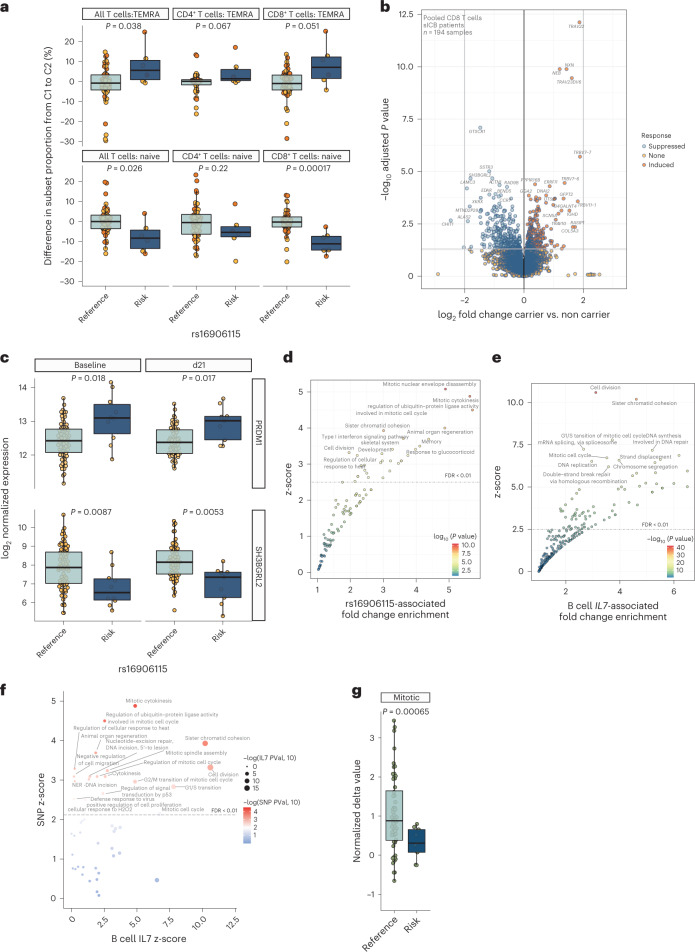
Fig. 4. Risk allele carriage is associated with T-cell-induced ICB responses.
a, Differences in subset proportion (depicted in facet name) between baseline untreated (C1) and immediately before the second cycle of treatment (C2) as determined by flow cytometry results assessing change in CD8+ T cell subset (depicted in facet name) with ICB treatment according to rs16906115 status; two-sided Wilcoxon rank-sum test, n = 54 patients. b, Volcano plot depicting results for DESEQ2 differential gene expression analysis of CD8+ T cell RNA-seq data, dichotomized by rs16906115 status; n = 194 samples across three cycles (untreated, C2 and C4) of sICB treatment, two-tailed Wald test. c, Example box plots of genes regulated by allele in sICB recipients, faceted by timepoint; two-sided t-test of normalized expression values, n = 86 patients at baseline, n = 69 patients at day 21. d, GOBP pathway analysis of genes suppressed in carriers of risk allele (as depicted in b); one-tailed hypergeometric test. e, GOBP pathway analysis of genes anti-correlated in patient CD8+ T cells with increasing B cell IL7 expression from the same blood samples; one-tailed hypergeometric test. f, Comparative analysis of z-scores (x axis: B cell IL7 effect, y axis: rs16906115 effect) from pathway analysis in d and e. g, Change in CD8+ T cell mitotic signature score post-sICB according to rs16906115 status; two-sided t-test, n = 65 patients. For box plots in a,c,g, the central line reflects the median value; the box corresponds to the 25–75% quartiles; the upper whisker extends to the largest value no farther than 1.5× IQR; and the lower whisker extends from the 25% quartile to the smallest value no farther than 1.5× IQR.