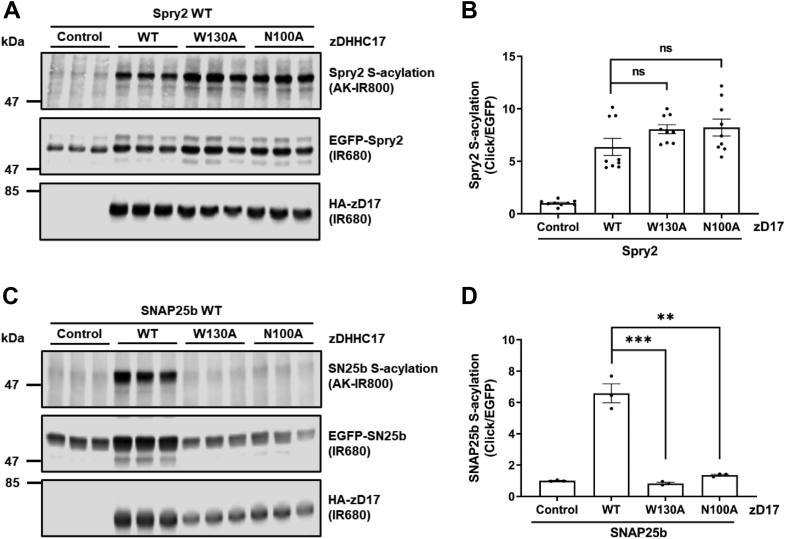
Figure 1.
S-acylation of Spry2 by zDHHC17 does not require Trp-130 or Asn-100. HEK293T cells were transfected with plasmids encoding either EGFP-tagged Spry2 or SNAP25b, together with either pEF-BOS-HA (referred to as “control” in the figure), HA-tagged zDHHC17 WT, zDHHC17 W130A, or zDHHC17 N100A. Cells were incubated with 100 μM palmitic acid azide for 4 h and labeled proteins reacted with alkyne (AK) IRdye-800 nm. EGFP- and HA-tagged proteins were labeled by immunoblotting using IRdye-680 nm secondary antibodies. A, representative images showing Spry2 S-acylation (top; AK-IR800) and Spry2 levels (middle; IR680) detected on the same immunoblot. For zDHHC17, HA (bottom; IR680) was revealed for the same samples on a different immunoblot. The positions of the molecular weight markers are shown on the left of all blots. B, graph showing mean Spry2 S-acylation levels after normalization. Error bars represent ± SEM; each replicate is shown with filled circles (n = 9 different cell samples for each condition). Unpaired t test was used to detect significant differences compared to the WT zDHHC17 samples; ns denotes nonsignificance (p > 0.05). C, representative image showing SNAP25b S-acylation (top; AK-IR800), SNAP25b levels (middle; IR680), and zDHHC17 levels (bottom; IR680). The positions of the molecular weight markers are shown on the left of all immunoblots. D, graph showing mean SNAP25b S-acylation levels after normalization. Error bars represent ± SEM; each replicate is shown with filled circles (n = 3 different cell samples for each condition). Unpaired t test was used to detect significant differences compared to the WT zDHHC17 samples (∗∗∗ denotes p < 0.001 and ∗∗ denotes p < 0.01).