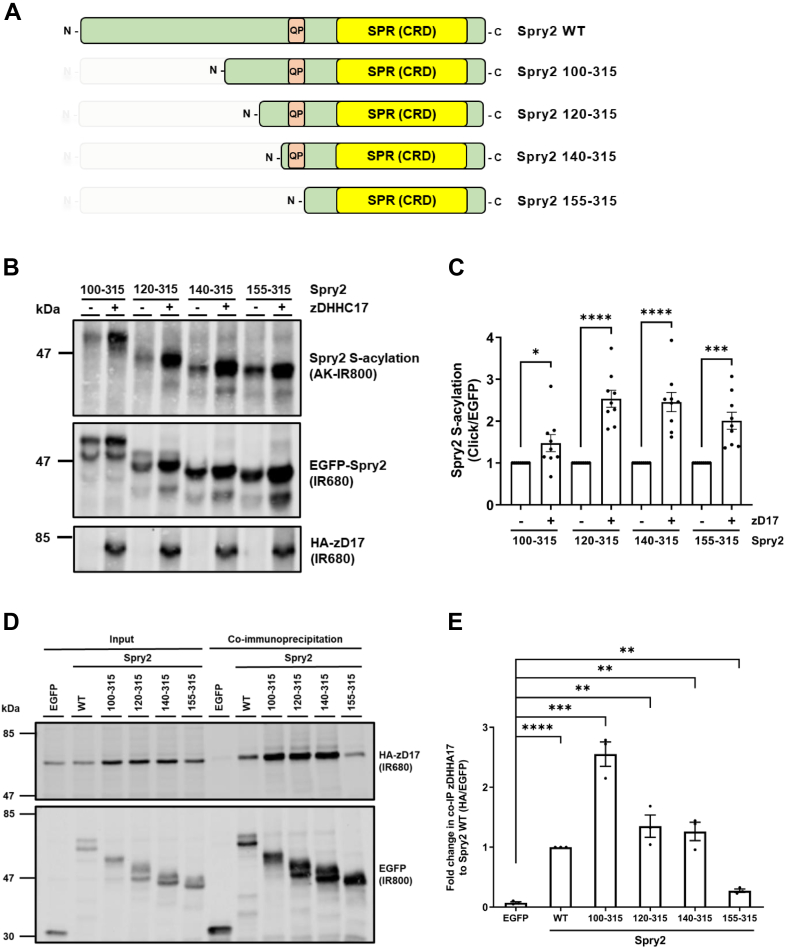
Figure 4.
Residues 155–315 of Spry2, which include the SPR domain, are sufficient for binding to, and S-acylation by, zDHHC17.A, schematic of the Spry2 constructs employed in click chemistry and co-immunoprecipitation assays: Spry2 100 to 315, 120 to 315, 140 to 315, and 155 to 315 of the mouse sequence (UniprotKB-Q9QXV8). All constructs have EGFP tags appended at the N terminus. Position of the zDABM containing proline-154 is denoted by “QP;” SPR denotes the Sprouty domain, which is also referred to as CRD (Cysteine-rich domain). B, HEK293T cells were transfected with plasmids encoding EGFP-tagged Spry2 100 to 315, Spry2 120 to 315, Spry2 140 to 315, or Spry2 155 to 315, together with either pEF-BOS-HA (referred to as “-” in the figure) or HA-zDHHC17 (referred to as “+” in the figure). Cells were incubated with 100 μM palmitic acid azide (C16:0-azide) for 4 h and labeled proteins reacted with alkyne (AK) IRdye-800 nm. EGFP- and HA-tagged proteins were labeled by immunoblotting using IRdye-680 secondary antibodies. Representative images showing Spry2 S-acylation (top; AK-IR800), Spry2 levels (middle; IR680), and zDHHC17 levels (bottom; IR680), detected on the same immunoblot. The positions of the molecular weight markers are shown on the left side of all immunoblots. C, graph showing mean Spry2 S-acylation levels after normalization against the corresponding control samples (pEF-BOS-HA). Error bars represent ± SEM; each replicate is shown with filled circles. Differences were analyzed by unpaired t test (∗∗∗∗ denotes p < 0.0001, ∗∗∗p < 0.001, ∗p < 0.05) (n = 9, for three independent experiments). D, HEK293T cells were cotransfected with HA-tagged zDHHA17 (a catalytically inert form of the enzyme) along with plasmids encoding for EGFP-tagged Spry2 100 to 315, Spry2 120 to 315, Spry2 140 to 315, and Spry2 155 to 315, or EGFP alone (as a control). Cell lysates were incubated with agarose beads conjugated to an EGFP antibody and coimmunoprecipitated proteins were analyzed by immunoblotting. Representative images showing zDHHA17 (top; IR680) and Spry2 (bottom; IR800) levels in the input and immunoprecipitated samples detected on the same immunoblot. The positions of the molecular weight markers are shown on the left side of all immunoblots. E, graph showing the mean fold change in coimmunoprecipitated zDHHA17 levels after normalization against Spry2 WT. Error bars represent ± SEM; each replicate is shown with filled circles. Differences were analyzed by unpaired t test compared to the EGFP control (∗∗∗∗ denotes p < 0.0001, ∗∗∗p < 0.001, ∗∗p < 0.01, n = 3 from three independent experiments).