TABLE 1.
Potential pharmacological targets and inhibitors targeting lipid uptake.
| Drug target | Notable inhibitors | Inhibitor description | IC50 | Development status | Related diseases | Chemical structure | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FATP2 | Lipofermata | — | 4.84 μM | Preclinical Stage | Melanoma |

|
Zhang et al. (2018) |
| CD36 | ABT-510 | TSP-1 mimetic drug | — | Phase 2 | Melanoma; Renal cell carcinoma, Lymphoma; Glioblastoma; Brain Tumor |

|
Campbell et al. (2010), Markovic et al. (2007), Nabors et al. (2010) |
| MAGL | ABX-1431 | An first-in-class irreversible inhibitor | 8 nM | Phase 2 | Neurological disorders |
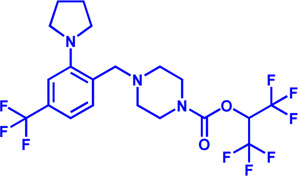
|
Cisar et al. (2018) |
| MAGL | MJN110 | Irreversible | 9.1 nM | Preclinical Stage | Diabetes; Neuropathy |
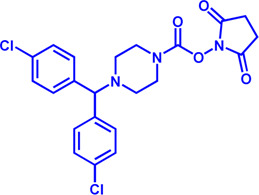
|
Wilkerson et al. (2016) |
| MAGL | JNJ-42226314 | Highly selective; Non-covalent; Reversible | 1.13 nM (Hela cells) | Preclinical Stage | Neuropathic and inflammatory pain |

|
Wyatt et al. (2020) |
| MAGL | JZL184 | The first selective MAGL inhibitor | 8 nM | Preclinical Stage | T2D; Glioblastoma |
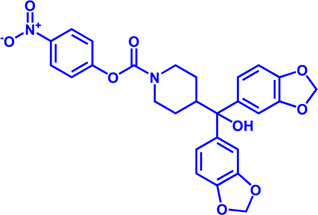
|
Taib et al. (2019), Walenna et al. (2020) |
| NPC1L1 | Ezetimibe | a selective inhibitor; Oral | — | FDA approved | Primary hyperlipidemia; Familial cholesterolemia |

|
Long et al. (2021), Rocha et al. (2022) |
The chemical information of small molecules is collected from Pubchem database (https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov), and 2D structures in the above diagram were drawn by Chemdraw software. IC50, half maximal inhibitory concentration.
