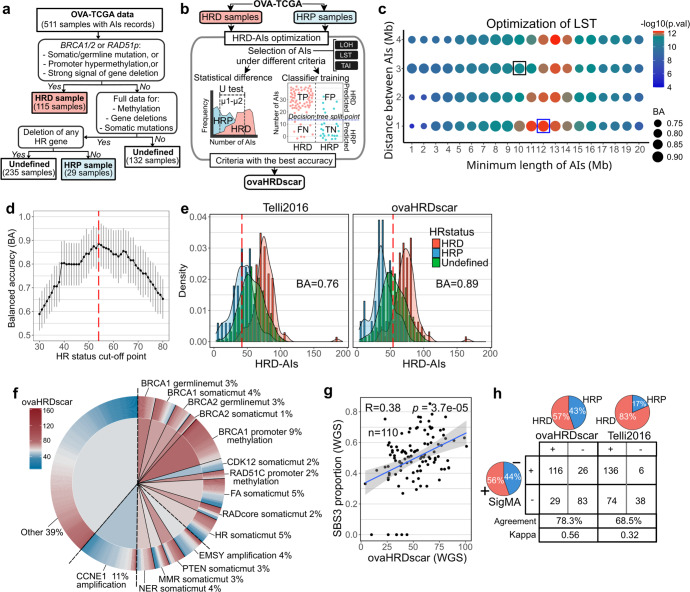
Fig. 2. Machine learning-aided detection of AIs associated with HRD shows improved accuracy and correlations with genomic features of HRD in HGSC.
a Selection criteria for annotating HRD, HRP and undefined HGSC samples in the OVA-TCGA. b A scheme of the approach used to generate accurate criteria for selecting HRD-AIs in HGSC samples. c For LST events, the size of dots represents the decision tree balanced accuracy (BA) of classifying HRD and HRP when selecting AIs of the corresponding criteria, the dot colors represent the statistical difference (U test, p-value) in abundance of AIs between HRD and HRP samples. The black box corresponds to the selection criteria proposed by Telli2016, the blue box correspond to the best BA and U test value. d Evaluation of ovaHRDscar cut-off to define HR-status. The black dots connected with a line correspond to the balanced accuracy (BA) of the classification of the annotated HRD and HRP samples using the given cut-off value, the 95% confidence intervals are shown in gray vertical lines, value of 54 (red dashed line) corresponds to the highest BA. e Density distribution of HRD-AIs according to Telli2016 and ovaHRDscar algorithms. The red dashed line represents the cut-off established to define the HR-status using Telli2016 (≥42) and using ovaHRDscar (≥54). The BA of classification of the annotated HRD and HRP is shown, density distribution colors correspond to the samples annotated as in the panel a. f Levels of ovaHRDscar in OVA-TCGA samples harboring different genetic or epigenetic alterations associated with HRD in HGSC4. The colors correspond to the ovaHRDscar; in the outer ring of the pie chart every line represents a sample and in the center of the pie chart the colors correspond to the average number of HRD-AIs per genetic or epigenetic alteration. For the somatic mutations (somaticmut) gene deletions were included. g Linear regression of the proportion of single base substitution signature 3 (SBS3) and the ovaHRDscar levels in PCAWG samples (Pearson r’ = 0.38). Blue line shows the regression line and the 95% confidence intervals are shown in gray. h The SBS3 status inferred using SigMA16 showing a higher agreement with ovaHRDscar (agreement = 78.3%, Cohen’s kappa = 0.56) than with the Telli2016 algorithm (agreement = 68.5%, Cohen’s kappa = 0.32). In the pie charts and table+ and - correspond to the number of HRD positive and HRD negative samples identified under each criterion, respectively. On the bottom is shown the number of samples and the level of agreement between the corresponding criteria.