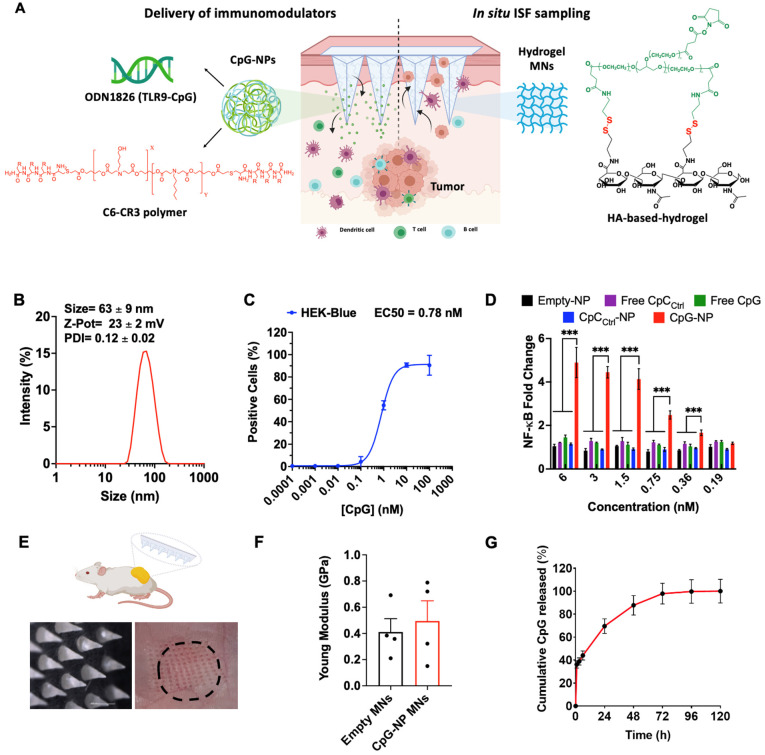
Figure 1.
Engineering a theranostic microneedle platform for management of skin cancer. A, Representative scheme of a hyaluronic acid (HA)-based microneedle platform for the delivery of immunomodulatory drugs (CpG-ODNs) complexed with poly (beta-amino ester)s (PBAEs) and simultaneous sampling of interstitial fluid (ISF) for recovery of immune cells ex vivo. B, Biophysical characterization of CpG-containing nanoparticles by dynamic light scattering. C, Quantification by flow cytometry of the cellular internalization of CpG-NPs by TLR9-expressing HEK 293 cells (n = 3 biologically independent samples). D, Dose-response of NF-kB produced by free CpG, free CpCCtrl, CpG-NPs, CpCCtrl-NPs and empty-NPs in HEK293 TLR9 reporter cell line in vitro (n = 4 biologically independent samples). E, Microscopy image of the HA-based MNs (scale bar = 500 µm) and representative image of mouse skin after in vivo administration of hydrogel MNs into the tumor. The dotted area indicates the tumor site. F, Characterization of the mechanical properties of HA-based MNs. A compression test was performed to compare the mechanical strength of empty MNs versus CpG-NP-loaded MNs. Data are mean ± s.e.m. (n = 4). G, In vitro CpG-NP release profile from the MNs assessed by tracking the fluorescence intensity of labeled NPs over time (pH = 7.4, 37 °C). Data are mean ± s.e.m. (n = 4).