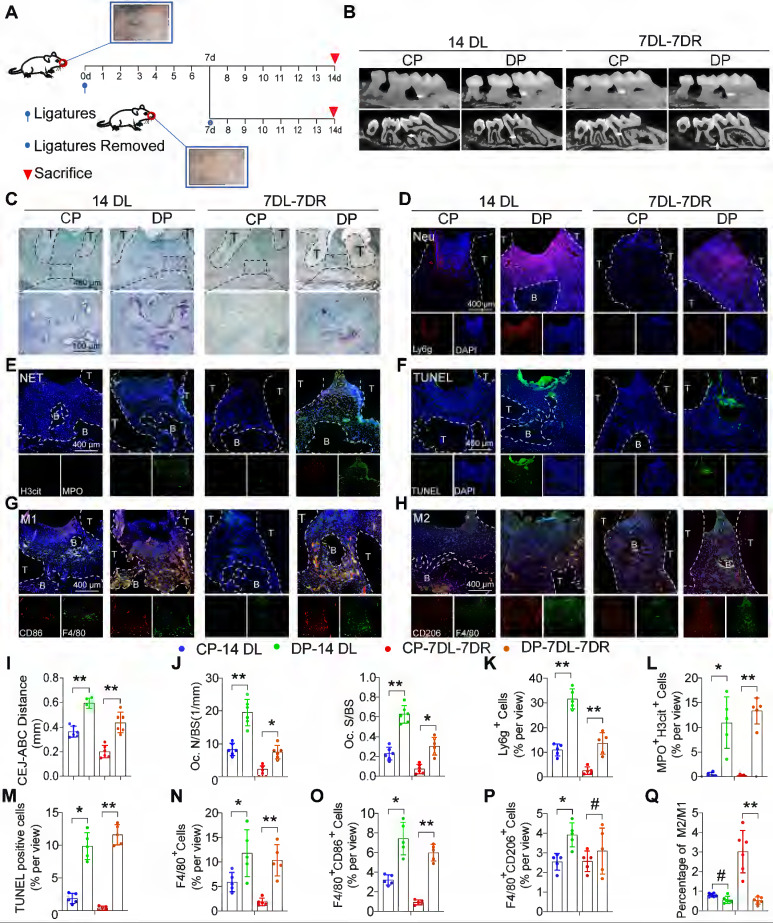
Figure 2.
Dysfunctional neutrophils and macrophages aggravate inflammatory damage and impair inflammation resolution in mice DP. (A) Schematic diagram showing the induction of the LIP (ligature-induced periodontitis) and LIP resolution models. (B) Representative 3D micro-CT scanning images and reconstructed sections (longitudinal direction of the maxillae). The distance of the Cemento-Enamel Junction (CEJ) to the Alveolar Bone Crest (ABC) in mm was analyzed. Arrowhead: the area of loss of alveolar bone. (C) Representative images of TRAP-stained paraffin sections. OC. N/ BS (osteoclast number per bone perimeter) and OC. S/BS alveolar bone surface covered by TRAP-positive osteoclasts) were used for quantitative analysis. (D) There are representative images of Ly6g positive neutrophils in the periodontium of control and diabetic LIP resolution mice. (E) Representative images of Cit-H3 (red) and MPO (green) positive NETs in the periodontium of control and diabetic LIP resolution mice. (F) Representative images of TUNEL staining. (G-H) Immunofluorescence staining of the periodontium, in which CD68 (green) positive represents macrophage, CD86 (red) positive represents M1 phenotype macrophage, and CD206 (red) positive represents M2 phenotype macrophage. (I-Q) Quantification of the distance of CEJ-ABC, OC. N/ BS, OC. S/BS, neutrophils, NET, TUNEL positive apoptotic cells, macrophage infiltration, and M1 and M2 polarization (n = 5 mice in the CP group and n = 5 mice in the DP groups). The results were presented as means ± S.D. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; #p > 0.05 by 2-tailed, unpaired Student's t test. T: Tooth, B: Bone of Alveolar, CP: chronic periodontitis, DP: diabetic periodontitis, 14DL: 14 days ligated; 7DL-7DR: 7 days ligated and 7 days with ligatures removed. The white dotted line indicates the boundary between the root and the alveolar bone and the gingiva.