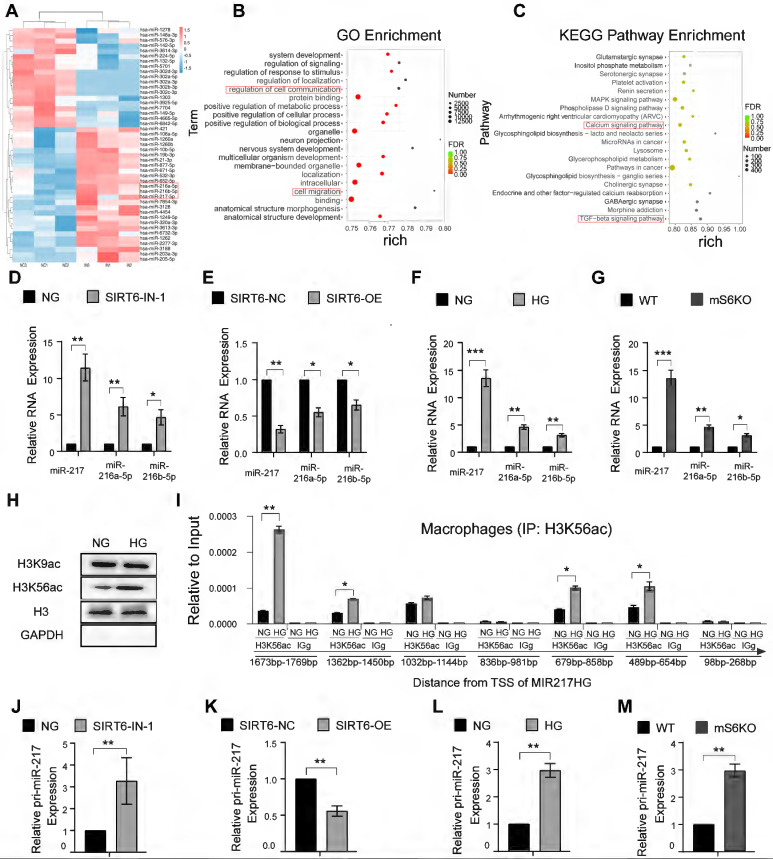
Figure 5.
SIRT6 inhibits transcription of miR-216a-5p-216b-5p-217 cluster through H3K56ac. (A) miRNA array analysis showed the differential miRNAs in macrophages after SIRT6 inhibition. (B) GO enrichment analysis of differential microRNA target genes. (C) KEGG Pathway enrichment analysis of differential microRNA target genes. (D) The high expression of miR216a-5p-216b-5p-217 cluster after SIRT6 inhibition. (E) The low expression of miR216a-5p-216b-5p-217 cluster after SIRT6 overexpression. (F) The high expression of miR216a-5p-216b-5p-217 cluster after high glucose stimulation. (G) Compared with BMMs of WT mice, Myeloid-specific SIRT6 deficiency mice exhibit high expression of miR216a-5p-216b-5p-217 clusters. (H) Western blot revealing the protein expression of H3K9ac and H3K56ac after high glucose stimulation. (I) H3K56ac was enriched around the TSS of MIR217HG in macrophages by ChIP-qPCR analysis. (J) The high expression of the pri-miR-217 after SIRT6 inhibition. (K) The low expression of pri-miR-217 after SIRT6 overexpression. (L) The high expression of the pri-miR-217 after high glucose stimulation. (M) Myeloid-specific SIRT6 deficiency mice exhibit high expression of pri-miR-217. The results were presented as means ± S.D. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p > 0.001 by 2-tailed, unpaired Student's t test.