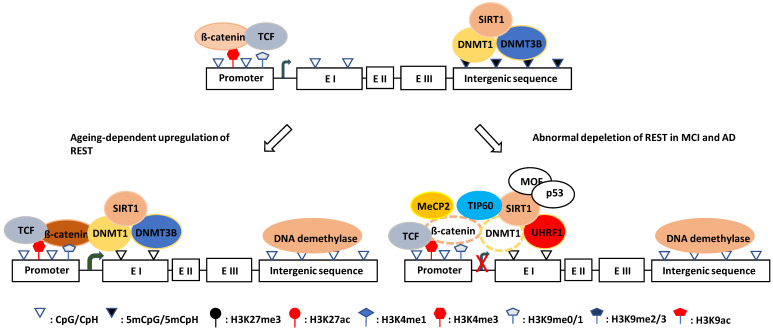
Figure 3.
Schematic illustration of the hypothesized mechanisms of REST expression in ageing and AD. (left) Upregulation mechanism: DNMT1 shifts from non-CGI region to CGI regulatory element under oxidative stress and forms a ß-catenin stabilizing complex to prevent DNA methylation and increase ß-catenin/TCF activity thereby increasing REST transcription. (Right) Downregulation mechanism: DNMT1 is degraded when acetylated by TIP60 and ubiquitinated by UHRF1. which can lead to ß-catenin destabilization. Whereas, MeCP2 can reduce availability of ß-catenin for binding to DNMT1. Both cases will downregulated REST transcription. MOF and p53 prevent SIRT1 expression, which can aggravate DNMT1 degradation.