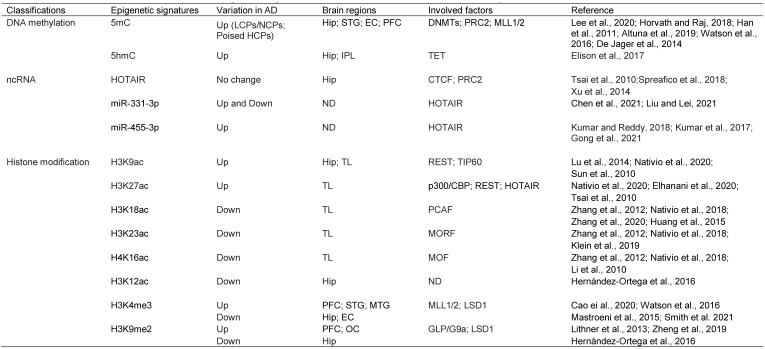
Table 1.
Overview of the epigenetic signatures in AD, their distribution and related enzymes or factors
Abbreviations: 5mC: 5-Methylcytosine; 5hmC: 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine; HOTAIR: HOX antisense intergenic RNA; H3K9ac: Histone H3 lysine 9 acetylation; H3K27ac: Histone H3 lysine 27 acetylation; H3K18ac: Histone H3 lysine 18 acetylation; H3K23ac: Histone H3 lysine 23 acetylation; H4K16ac: Histone H4 lysine 16 acetylation; H3K12ac: Histone H3 lysine 12 acetylation; H3K4me3: Histone H3 lysine 4 trimethylation; H3K9me2: Histone H3 lysine 9 dimethylation; LCPs: low-intensity CpG promoters; NCPs: non-CGI promoters; HCPs: High-intensity CpG promoters; Hip: Hippocampus; STG: Superior temporal gyrus; EC: Entorhinal cortex; PFC: Prefrontal cortex; IPL: inferior parietal lobe; TL: temporal lobe; MTG: Medial temporal gyrus; OC: Occipital cortex; DNMT: DNA methyltransferase enzyme; PRC2: Polycomb repressive complex 2; MLL1/2: Mixed lineage leukemia1/2; TET: Ten-eleven translocation; CTCF: CCCTC-binding factor; REST: Repressor element 1 (RE1)-silencing transcription; TIP60: Tat-interacting protein of 60 kDa; p300/CBP: p300/CREB binding protein; PCAF: p300/CBP-associated factor; MORF: MOZ-related Factor; MOF: Males absent on the first; ND: Not determined; LSD1: Lysine-specific demethylase 1.