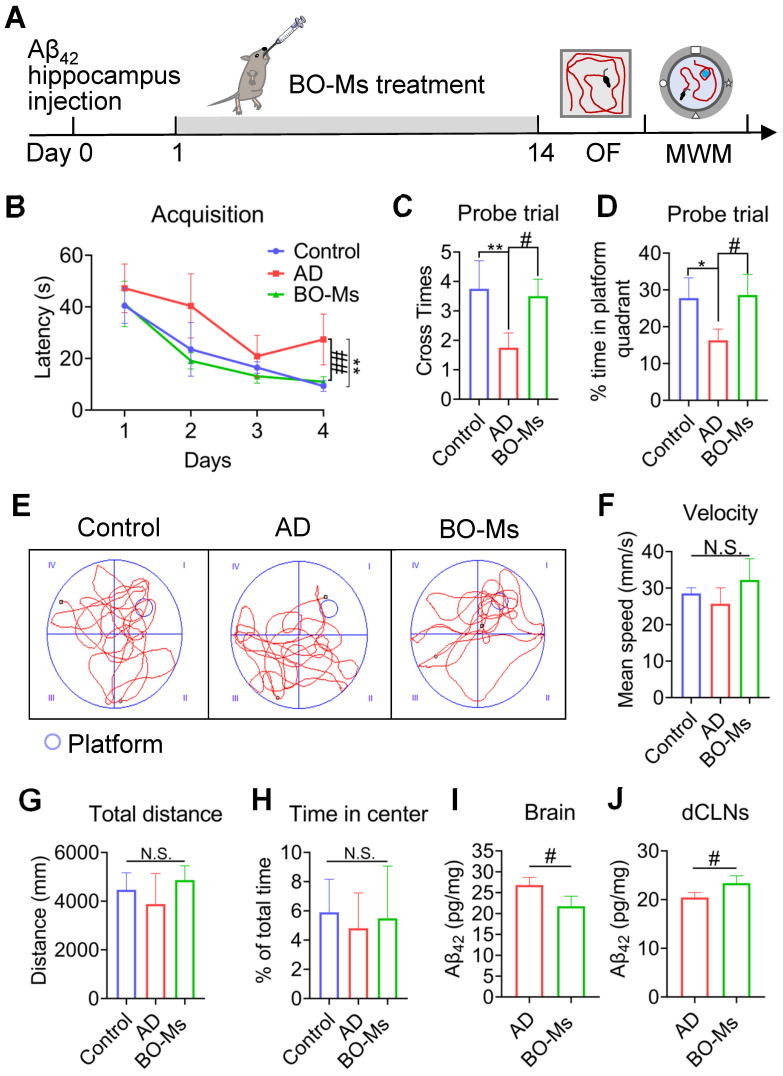
Figure 6.
BO-Ms improved memory deficits in AD mice. (A) Timeline of BO-Ms treatment in AD mice. (B) Escape latency to the platform during the training trails in a Morris water maze. **p < 0.01, vs. control group. ##p < 0.01, vs. AD group. n = 6 mice per group. Data are means ± SEM. (C) The number of target platform crossings in the probe test. **p < 0.01, vs. control group. n = 6 mice per group. #p < 0.05, vs. AD group. n = 6 mice per group. Data are means ± SEM. (D) Time spent in the target quadrant in the probe test. *p < 0.05, vs. control group. n = 6 mice per group. #p < 0.05, vs. AD group. n = 6 mice per group. Data are means ± SEM. (E) Representative track images of mice in the probe test. (F) Mean swimming velocity of mice. N.S. = not significant. (G) Total distance in open field arena. N.S. = not significant. (H) Percentage of time in the center of the open field arena. N.S. = not significant. (I) Content of Aβ42 oligomers in the brains measured by ELISA. #p < 0.05, vs. AD group. n = 3 mice per group. Data are means ± SEM. (J) Content of Aβ42 in the dCLNs measured by ELISA. #p < 0.05, vs. AD group. n = 3 mice per group. Data are means ± SEM.