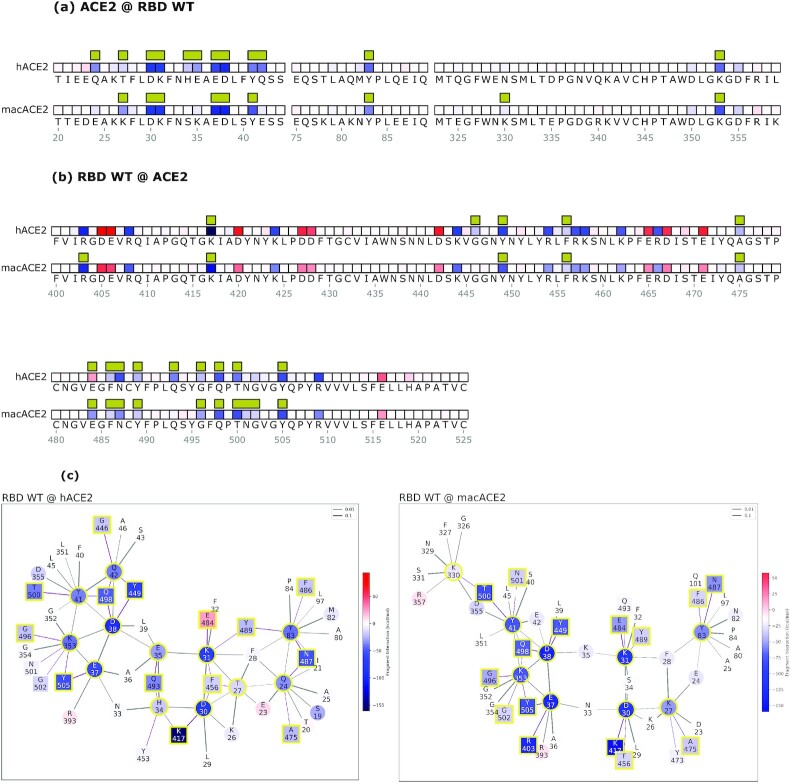
Fig. 3.
Mechanistic characterization of the Wuhan spike binding to the human ACE2 (hACE2) and R. macrotis ACE2 (macACE2). Data are plotted on the ACE2 primary structure (a), and on the Wuhan spike RBD (b), when binding to the human (hACE2) and the bat (macACE2) receptor. Amino acid residues are labeled with letters and numbered. Interface residues are highlighted with a yellow bar, red tiles are repulsive residues, and blue tiles are attractive residues; see the rest of the figure for energy scales. The interaction networks (c) represent the hACE2-spike system on the left, and macACE2-spike on the right; circles are ACE2 residues, squares are spike residues. Interface residues are highlighted with a yellow bar, red tiles are repulsive residues, and blue tiles are attractive residues. Bonds are purple when intermolecular or black when intramolecular, and their thickness represents the strength of the FBO between residues.