Table 4.
Average percent bias, empirical SE, and CP of the 95 CI of
CI of  , and
, and  across 1000 simulation replicates
across 1000 simulation replicates
| No. of testing sites | Testing site size | Method |

|

|

|

|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bias (SE) | CP | Bias (SE) | CP | Bias (SE) | CP | Bias (SE) | CP | |||
| 50 | 30 | IndCov | 0.2 (0.134) (0.134) |
0.964 | 0.8 (0.110) (0.110) |
0.992 | 3.9 (0.124) (0.124) |
0.976 | 0.0 (0.071) (0.071) |
0.952 |
| ExchCov | 0.6 (0.125) (0.125) |
0.958 | 2.5 (0.075) (0.075) |
0.971 | 1.1 (0.085) (0.085) |
0.952 | 0.4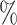 (0.094) (0.094) |
0.958 | ||
| ExchTwoS |
 0.1
0.1 (0.066) (0.066) |
0.949 |
 0.1
0.1 (0.067) (0.067) |
0.944 | 0.4 (0.075) (0.075) |
0.938 | 0.1 (0.053) (0.053) |
0.945 | ||
| 50 | 60 | IndCov | 0.1 (0.088) (0.088) |
0.965 |
 0.7
0.7 (0.077) (0.077) |
0.991 | 4.1 (0.087) (0.087) |
0.980 | 0.0 (0.051) (0.051) |
0.950 |
| ExchCov | 0.5 (0.085) (0.085) |
0.958 | 1.5 (0.055) (0.055) |
0.961 | 1.3 (0.057) (0.057) |
0.966 | 0.3 (0.067) (0.067) |
0.955 | ||
| ExchTwoS | 0.1 (0.045) (0.045) |
0.955 | 0.1 (0.045) (0.045) |
0.956 | 0.8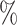 (0.050) (0.050) |
0.939 | 0.0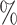 (0.039) (0.039) |
0.946 | ||
| 100 | 30 | IndCov |
 0.5
0.5 (0.089) (0.089) |
0.937 |
 5.0
5.0 (0.079) (0.079) |
0.983 | 4.2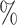 (0.086) (0.086) |
0.967 | 0.1 (0.048) (0.048) |
0.948 |
| ExchCov |
 0.2
0.2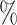 (0.082) (0.082) |
0.949 |
 3.6
3.6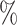 (0.056) (0.056) |
0.958 | 2.2 (0.059) (0.059) |
0.945 | 0.3 (0.063) (0.063) |
0.957 | ||
| ExchTwoS |
 0.1
0.1 (0.046) (0.046) |
0.959 |
 1.2
1.2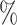 (0.051) (0.051) |
0.952 | 0.8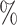 (0.055) (0.055) |
0.940 | 0.2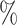 (0.037) (0.037) |
0.961 | ||
| 100 | 60 | IndCov |
 0.4
0.4 (0.059) (0.059) |
0.953 |
 5.1
5.1 (0.052) (0.052) |
0.978 | 3.8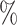 (0.056) (0.056) |
0.969 | 0.1 (0.035) (0.035) |
0.939 |
| ExchCov |
 0.1
0.1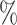 (0.057) (0.057) |
0.954 |
 3.2
3.2 (0.039) (0.039) |
0.941 | 1.8 (0.040) (0.040) |
0.953 | 0.2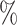 (0.045) (0.045) |
0.956 | ||
| ExchTwoS |
 0.2
0.2 (0.033) (0.033) |
0.948 |
 0.9
0.9 (0.034) (0.034) |
0.940 | 0.4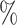 (0.035) (0.035) |
0.955 | 0.0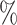 (0.027) (0.027) |
0.950 | ||
A mixed-effects model is used to estimate the treatment probability and the effects of cluster-level unmeasured confounder on the treatment are generated from a skewed normal distribution with location parameter to be  1, scale parameter being 0.1 and shape parameter equals to 100. For the one-stage method, we consider the following situations: (1) using a working independent covariance matrix (IndCov); (2) using a working exchangeable covariance matrix for within subject correlation and assume independence between subjects (ExchCov). For the two-stage method, we consider using a working exchangeable covariance matrix for the first stage cluster-specific MSMs and combine the results using mixed-effects meta-analysis (ExchTwoS).
1, scale parameter being 0.1 and shape parameter equals to 100. For the one-stage method, we consider the following situations: (1) using a working independent covariance matrix (IndCov); (2) using a working exchangeable covariance matrix for within subject correlation and assume independence between subjects (ExchCov). For the two-stage method, we consider using a working exchangeable covariance matrix for the first stage cluster-specific MSMs and combine the results using mixed-effects meta-analysis (ExchTwoS).
