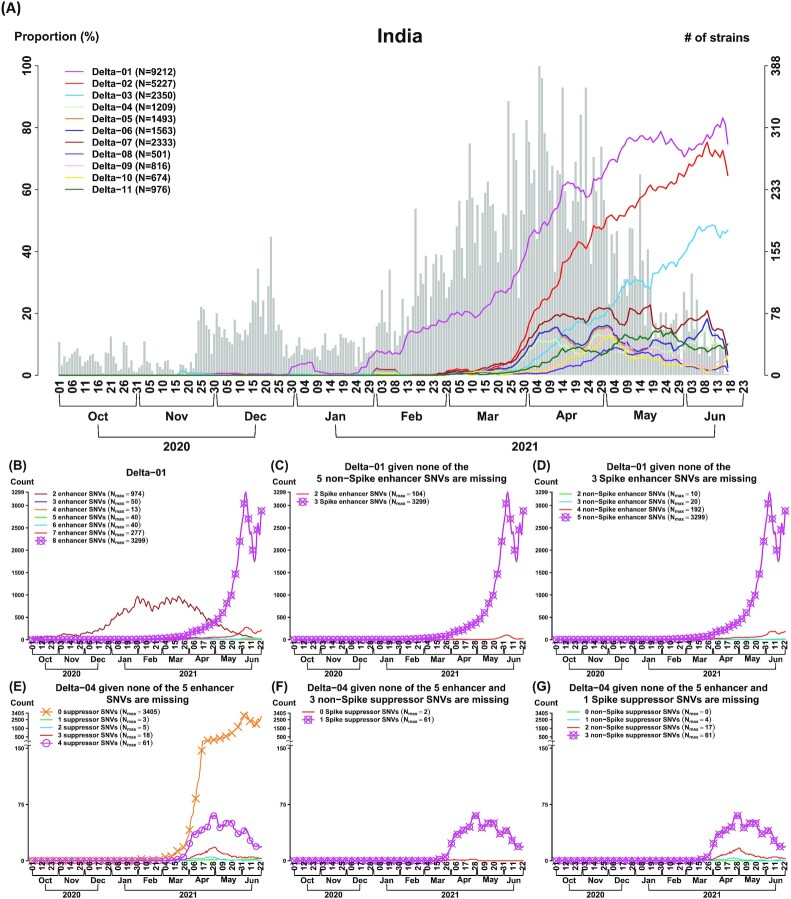
Fig. 2.
The CSS analysis identifies multiple Delta subtypes with differential temporal trajectories (n = 2,119 K genomes as of 2021 June 23). (A) Eleven Delta (aka B.1.617.2) CSSs are identified in India. Three CSSs (Delta-01 to 03) have an increasing temporal trajectory and eight CSSs (Delta-04 to 11) have a much lower temporal trajectory, revealing that CSSs provide a more detailed information for the subtypes and their transmission patterns for Delta. (B to D) Missing transmission enhancer SNVs causes a dramatically decrease in the temporal trajectory in the enhanced CSS Delta-01. The curve with a symbol o indicates the temporal trajectory of Delta-01. The curve with a symbol x indicates the Delta-01 variant with the maximum temporal trajectory among the different Delta-01 variants without or with a missing of specific SNVs. Nmax indicates the maximum number of strains in a temporal trajectory. Delta-01 carries 8 transmission enhancer SNVs (Table 1), where there are 3 SNVs in the spike protein and 5 SNVs in the non-spike proteins. In (B), it shows that missing any of 8 transmission enhancer SNVs causes a decrease in the temporal trajectory in Delta-01. In (C), it shows that missing any of 3 transmission enhancer SNVs in the spike protein causes a decrease in the temporal trajectory in Delta-01. In (D), it shows that missing any of 5 transmission enhancer SNVs in the non-spike proteins causes a decrease in the temporal trajectory in Delta-01. When any of the transmission enhancer SNVs are missing (the curve without a symbol x), the temporal trajectories are dramatically reduced. This phenomenon explains that the transmission enhancer SNVs work cooperatively. (E to G) Missing all of the transmission suppressor SNVs causes an increase in the temporal trajectory in the suppressed CSS Delta-04. The curve with a symbol o indicates the temporal trajectory of Delta-04. The curve with a symbol x indicates the Delta-04 variant with the maximum temporal trajectory among the different Delta-04 variants without or with a missing of specific SNVs. Nmax indicates the maximum number of strains in a temporal trajectory. Delta-04 carries five transmission enhancer SNVs and four transmission suppressor SNVs (Table 1). Among the four suppressor SNVs, one is located in the spike protein and the other three are located in the non-spike proteins. In (E), it shows that missing all of the four transmission suppressor SNVs causes an increase in the temporal trajectory. In (F), it shows that missing the only transmission suppressor SNV in the spike protein (conditional on that the three non-spike suppressor SNVs are remained) does not cause an increase in the temporal trajectory. In (G), it shows that missing any of the transmission suppressor SNVs in the non-spike proteins (conditional on that the spike suppressor SNV is remained) does not cause an increase in the temporal trajectory. When all of the four transmission suppressor SNVs are remained, the temporal trajectory of Delta-04 is dramatically reduced. This phenomenon illustrates that transmission suppression can be contributed by a single spike SNV or a set of transmission suppressor SNVs.