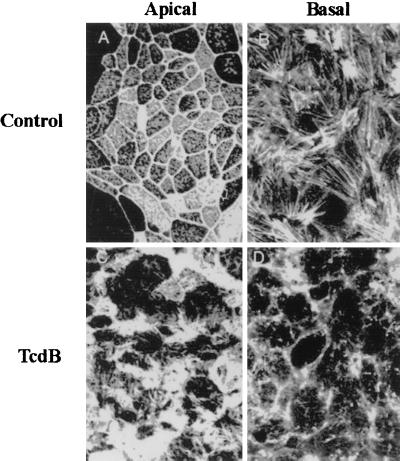
FIG. 2.
C. difficile toxins influence F-actin architecture in the apical and basal poles of T84 intestinal epithelial cells. F-actin distribution in control (serum-free medium) (top panels) or TcdB (bottom panels)-exposed monolayers was determined 2 h after toxin incubation. Confocal microscopic localization of F-actin in en face optical sections reveals a normal F-actin distribution in the apical membrane and as perijunctional F-actin rings (top left). Prominent stress fibers are observed in the base of cells (top right). Incubation with this toxin induced disruption and disorganization of F-actin in both the apical (bottom left) and basal (bottom right) poles of T84 cells. Note the loss of apical perijunction F-actin rings and basal stress fibers. Representative data from six individual experiments are shown.